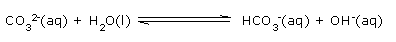Reaction to show weak acid and strong base
Reaction to show weak acid and strong base
Potassium cyanide is the salt of the very strong base potassium hydroxide and the very weak hydrocyanic acid (pKa = 9.31, Ka = 4.9 × 10−10 mol dm−3). The hydrated potassium ion shows no acidic behavior, but the cyanide ion is a strong conjugate base of the very weak hydrocyanic acid (HCN) which interacts with water to generate hydroxide ions. Hydrocyanic acid (pKa = 9.4) is weaker than ethanoic acid (pKa = 4.76), so the equilibrium is more on the right, more OH−, and so the pH is more alkaline, i.e. over 9.

Sodium carbonate is the ‘salt’ of the strong base sodium hydroxide and the very weak ‘carbonic acid’. Again the hydrated sodium ion shows no acidic character but the carbonate ion is a strong conjugate base of a the weak ‘carbonic’ acid, so an acid‐base hydrolysis reaction occurs to generate hydroxide ions to raise the pH.