Reactions of neutral ferric chloride solution:
Phenols form characteristic coloured iron complexes when treated with neutral ferric chloride solution. E.g. phenol & resorcinol - violet colour, catechol-green etc.

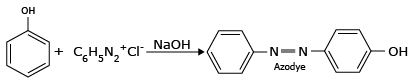
Azo dye formation:
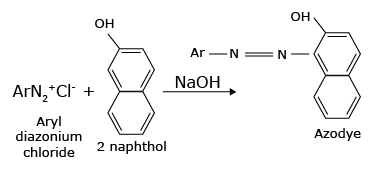
Aryldiazonium salts react with aromatic rings of phenols to form highly coloured azo compounds. These reactions are called coupling reactions.
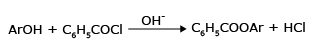
Benzoylation:
Phenols react with benzoyl chloride in presence of NaOH, to form esters (fruity odour)
Reactions of primary amines:
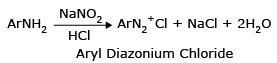
1. Diazotisation:
At low temperature (0-50°C) aromatic primary amine dissolves in strong acids (HCl & H2SO4) and reacts with nitrous acid (NaNO2+HCl) to form water soluble diazonium salts.
Aliphatic primary amines do not form stable diazonium salts under similar condition. They react with nitrous acid to yield alcohols and nitrogen (causes rapid foaming).
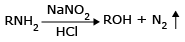
2. Azo dye formation for aromatic primary amines:
Aryldiazonium salts react with aromatic rings of phenols to form highly coloured azo compounds. These reactions are called coupling reactions.
3. Benzoylation:
Primary aromatic amines react with benzoyl chloride in presence of NaOH, replacing the H atom attached to the N atom with the benzoyl group to give anilides.

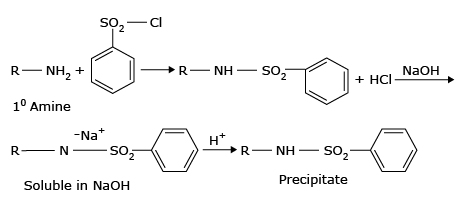
4. Hinsberg reaction:
Hinsberg reagent is called benzenesulfonyl chloride. Primary aliphatic amines on reaction with benzenesulfonyl chloride & NaOH give N-alkylsulphonamide which contains an acidic hydrogen and hence dissolves in NaOH solution to form the soluble sodium salt. The solution thus obtained on acidification gives a precipitate of free sulfonamide which is insoluble in HCl.