Electronegative Halide
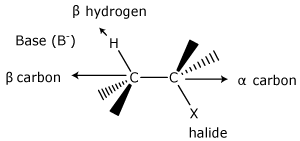
The α –carbon is bonded to the substituent, (halide in this case). The β –carbon is always bonded to the α –carbon. The β –hydrogen is bonded to the β –carbon. β –hydrogen is easily removed by a base because electron density in the molecule is pulled to the electronegative halide, leaving the β –hydrogen with a slight positive charge.