Examples
Ex 1:
In figure m ∥ n and angles 1 and 2 are in the ratio 3 ∶ 2. Determine all the angles from 1 to 8.
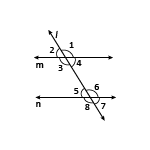
Sol:
- It is given that ∠1 ∶ ∠2 = 3 ∶ 2.
- So, let ∠1 = 3x° and ∠2 = 2x°.
- But, ∠1 and ∠2 form a linear pair.
| ∴ ∠1 + ∠2 | = | 180° |
| ⇒ 3x° + 2x° | = | 180° |
| ⇒ 5x° | = | 180° |
| ⇒ x | = | 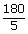 |
| = | 36° | |
| ∴ ∠1 | = | 3x° = (3 × 36)° = 108° |
| and, ∠2 | = | 2x° = (2 × 36)° = 72° |
| Now, ∠1 | = | ∠3 and ∠2 = ∠4 [vertically opposite angles] |
| ∴ ∠4 | = | 72° and ∠3 = 108° |
| Now, ∠6 | = | ∠1 and ∠4 = ∠7 [Corresponding angles] |
| ⇒ ∠6 | = | 72° and ∠7 = 108° [∵ ∠2 = 72°] |
| Again, ∠5 | = | ∠7 and ∠8 = ∠6 [Vertically opposite angles] |
| ∴ ∠5 | = | 108° and ∠8 = 72° |
| Hence, ∠1 | = | 108°, ∠2 = 72°, ∠3 = 108°, ∠4 = 72°, ∠5 = 108°, ∠6 = 72°, ∠7 = 108° and ∠8 = 72°. |
Ex 2:
In figure AB ∥ CD. Determine x.
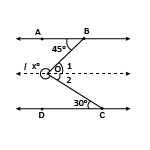
Sol:
- Through O, draw a line l parallel to both AB and CD. Then,
- ∠1 = 45° and ∠2 = 30° [Alternate ∠s]
| ∴ ∠BOC | = | ∠1 + ∠2 |
| ⇒ ∠BOC | = | 45° + 30° |
| = | 75° | |
| Clearly, x | = | reflex ∠BOC |
| ∴ x | = | 360° – ∠BOC |
| ⇒ x | = | 360° – 75° |
| = | 285° | |
| Hence, x | = | 285°. |
Ex 3:
In figure AB ∥ CD and AE ∥ CF, ∠FCG = 90° and ∠BAC = 120°. Find the value of x, y and z.
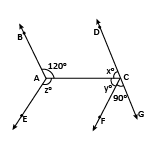
Sol:
- Alternate interior angle.
| ∠BAC = ∠ACG | = | 120° |
| ∠ACF + ∠FCG | = | 120° |
| So, ∠ACF | = | 120° – 90° = 30° |
| Linear pair | ||
| ∠DCA + ∠ACG | = | 180° |
| ∠x | = | 180° – 120° |
| = | 60° | |
| ∠BAC +∠BAE + ∠EAC | = | 360° |
| ∠CAE | = | 360° – 120° – (60° + 30°) |
| = | 150° | |