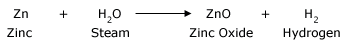Reaction of non–metals with oxygen
oxide.jpg) Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur combusts in pure oxygen with a brilliant blue flame producing sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur combusts in pure oxygen with a brilliant blue flame producing sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Non–metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides. For example carbon forms an acidic oxide CO2, sulphur forms SO2 and phosphorus forms P2O5.
The neutral non–metal oxides are carbon monoxide (CO), water (H2O), nitricoxide (NO), and nitrous oxide (N2O). The non–metal oxides are covalent in nature, which are formed by the sharing of electrons. The acidic oxides of non–metals dissolve in water to form acids. They turn blue litmus solution to red.
Non–metals do not react with water or steam to evolve hydrogen gas. This is because non–metals cannot give electrons to reduce the hydrogen ions of water into hydrogen gas. Non–metals do not react with dilute acids. In other words non–metals do not displace hydrogen from acids. For example carbon, sulphur and phosphorus do not react with dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) or dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
Metal oxides
 Reactivity of sodium metal
Sodium reacts with oxygen in the air and produces a layer of oxide
– Sodium oxide. Sodium oxide is like rust for sodium, which corrodes the metal.
Reactivity of sodium metal
Sodium reacts with oxygen in the air and produces a layer of oxide
– Sodium oxide. Sodium oxide is like rust for sodium, which corrodes the metal.
Sodium reacts with oxygen or air at ordinary room temperature. The resultant is sodium oxide. Sodium is a highly reactive metal and catches fire easily when exposed to air.
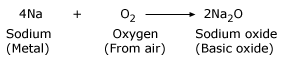
All metals react with water to form metal oxides and metal hydroxides. Hydrogen gas is released in this reaction. Metal oxides are basic in nature; when dissolved in water they form alkaline solution. Not all metals react with water at room temperature. Some metals react with cold water, some metals react with hot water, and other metals react with steam. There are some metals that do not react with water at all.
Zinc metal reacts with steam. Zinc forms ZnO (zinc oxide) and hydrogen are formed.