Alkenes
The compounds containing the multiple bonds are named according to the following rules.
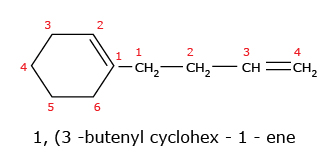
- The longest continuous chain containing the carbon atoms involved in the multiple bonds
is selected.
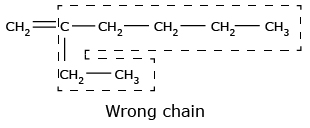
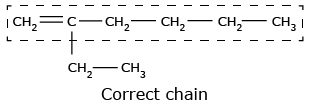
- While writing the name of the alkene or alkyne, the suffix 'ane' of the corresponding alkane is replaced by 'ene' or 'yne' respectively.
- If the multiple bond occurs twice in the parent chain, the alkene and alkyne are called diene and diyne respectively.
- The numbering of atoms in parent chain is done in such a way that the carbon atom
containing the double or triple bond gets
the lowest number.
Correct
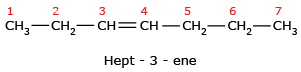 Wrong
Wrong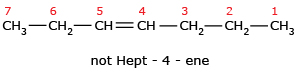
- All the rules for naming the side chains or substituents are similar to alkanes.
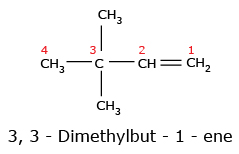
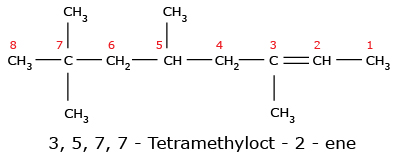
Important Note: If both double and triple bonds are present in a parent chain, the following rules should be remembered.
- The terminal 'e' in the name is dropped when it is followed by the suffix beginning with 'a', 'i', 'o', 'u' or 'y'.
- Numbers as low as possible are given to double bond and triple bond as a set, even
though this may at times give –yne a lower number than
–ene. However, if a choice is there, preference for lower
locants
is given to double bond(–ene).
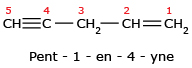
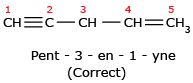 The name cannot be Pent – 2 – en – 4 – yne because lowest set is 1,3 rather than 2,4.
The name cannot be Pent – 2 – en – 4 – yne because lowest set is 1,3 rather than 2,4.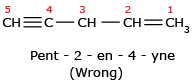 Here are some more examples:
Here are some more examples: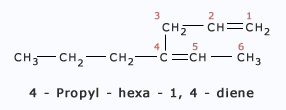
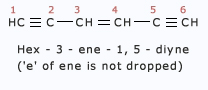
- In case of cyclic alkenes, the position of double bond is always given the number
1.
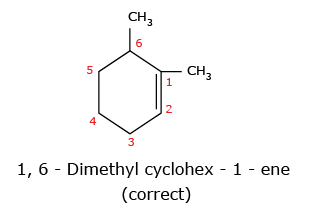
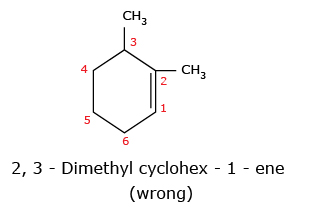 The name of the compound cannot be 2,3 – Dimethyl cyclohex – 1 – ene because of lowest set rule. When we compare the set (1,6) with (2,3), the former is correct because 1 is lower than 2.
The name of the compound cannot be 2,3 – Dimethyl cyclohex – 1 – ene because of lowest set rule. When we compare the set (1,6) with (2,3), the former is correct because 1 is lower than 2.