When the vectors act along the same direction i.e., θ = 0°:

When the vectors act along opposite directions i.e., θ = 180°:
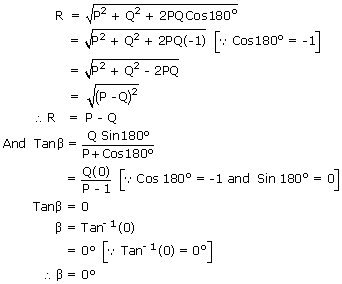
Thus the magnitude of the resultant of two vectors acting in the opposite directions is equal to the difference in the magnitudes of the vectors. The resultant acts in the direction of the larger vector.