In general, how does matter change from one state to another? As you may have guessed, changes in energy are involved. Changes of state are physical changes in matter. They are reversible changes that do not involve changes in chemical properties of the matter. Common changes of state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization. In general, how does matter change from one state to another? As you may have guessed, changes in energy are involved. Changes of state are physical changes in matter. They are reversible changes that do not involve changes in matter's chemical makeup or chemical properties. Common changes of state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization.
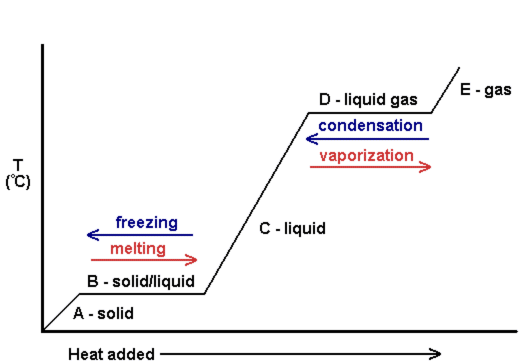
Changes between solids and liquids(from the graph, between A and C): The process in which a liquid changes to a solid is called freezing. Energy is taken away during freezing. The temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid is its freezing point. The process in which a solid changes to a liquid is called melting. Energy is added during melting. The melting point is the temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid.
Changes between liquids and gases (from the graph, between C and E): If water gets hot enough, it starts to boil. Bubbles of water vapor are formed in the boiling water. The bubbles rise through the water and escape from the pot as steam. The process in which a liquid boils and changes to a gas is called vaporization. The temperature at which a liquid boils is its boiling point. A liquid can also change to a gas without boiling. This process is called evaporation. It occurs when particles at the exposed surface of a liquid absorb just enough energy to pull away from the liquid and escape into the air. This happens faster at warmer temperatures. Energy is added during evaporation and vaporization. The process in which a gas changes to a liquid is called condensation. Energy is removed during condensation, changing a gas to a liquid.