During refraction of light, which of the following quantities does not change : velocity, wavelength, frequency and amplitude ?The atmospheric pressure is 80 cm of Hg. Express it in N m–2 Use: density of Hg = 13.6 g cm–3, g = 9.8 m s–2?
The frequency of light does not change on refraction.
A ray of light falls normally on a glass slab. What is the angle of refraction?
| For normal incidence, angle of incidence i | = | 0° |
| ∴ angle of refraction r | = | 0° |
Refractive index of water is 4/3. Calculate the speed of light in water. Speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m s–1 ?
| ∴ Refractive index of water | = | (Speed of light in vacuum) / (Speed of light in water) |
| 4/3 | = | ((3 × 108) ms–1)/(Speed of light in water) |
| or Speed of light in water | = | (3/4) × 3 × 108 ms–1 |
| = | 2.25 × 108 ms– 1 |
A ray of light strikes a glass slab 7 cm thick, making an angle of incidence equal to 30o. Construct the ray diagram showing the refracted ray and the emergent ray through the glass block. The refractive index of glass is 1.5. Also calculate the lateral displacement of the ray?
The ray diagram is given in below.
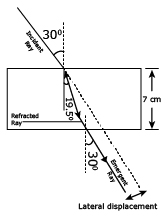
| ∴ sin r | = | (sin i)/μ |
| = | (sin 30°)/1.5 | |
| = | (1/2)/1.5 | |
| = | 1/3 | |
| or r | = | 19.5° |
Lateral displacement = 1cm nearly (on proper scale)×
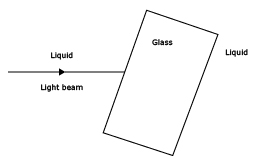
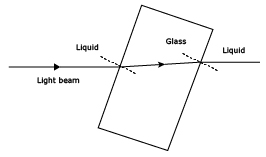
(i) (b) If light speeds up in going from liquid to glass (i.e., μglass > μliquid), it will bend away from tne normal at the point of incidence on the first surface in passing from liquid to glass, while it will bend towards the normal at the second surface in passing from glass to liquid. The ray diagram is shown in below figure.
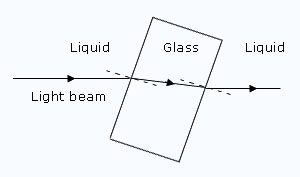
 i = 0°, then
i = 0°, then  r = 0°).
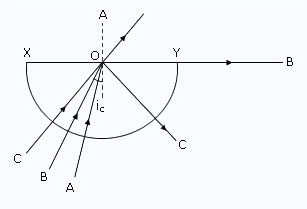
r = 0°).The diagram below shows the section of a semi–circular glass block having centre at O. A, B, and C are monochromatic rays of light of the same colour. On the diagram, mark the critical angle by ic. Draw the paths of rays A and C after they strike the edge XY. Name the phenomena which the paths of rays A and C (into and out of the block) exhibit?
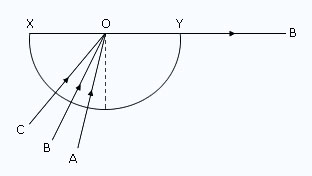
The completed diagram is shown in below figure.
The critical angle has been marked as ic.
The ray A suffers refraction from glass to air.
The ray C suffers total internal reflection.