Derivation of Bohr radii and energy for hydrogen atom
Historically, the first prediction of the radii and energy levels for a hydrogen atom was by Neils Bohr in 1913.
For this work, he received the Nobel Prize in physics in 1922. Bohr used the following assumptions about the hydrogen atom.
- The wavelength of the electron was given by the de Broglie relation,
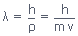
- The stable electron orbits for the hydrogen atom are restricted to those with an integer number of wavelengths
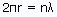
- The potential energy of the electron is given by the Coulomb's law, where we generalize the result to hydrogen-like atoms and ions
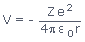
The virial theorem for particles under a central force field as for electrostatic attraction states
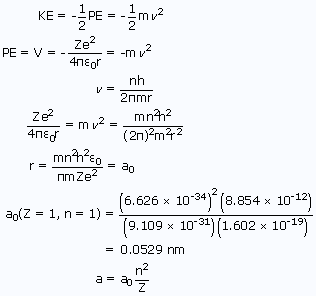
The energy is given by
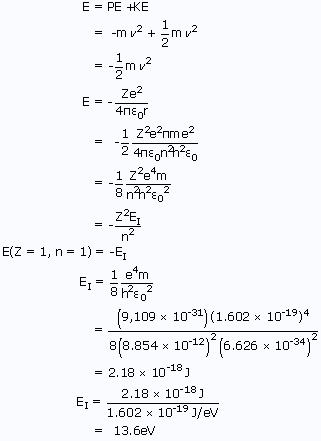
Thus, by using the above relations, radius and energy of a 1st orbit of the hydrogen atom are found out.
Similarly, by replacing 'n' values in the equation the respective radii and energy can be found out.
Energy difference between two different orbitals of hydrogen atom can be known by using the formula
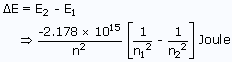
Where n1 and n2 are the orbits from which energy differences has to be calculated.