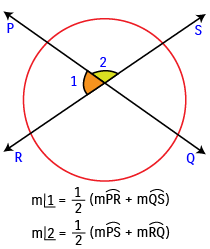
(i) If two secants intersect in the interior of a circle, then the measure of an angle formed is one half the sum of the measure of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle.
Example:

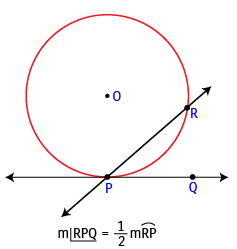
(ii) If a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of contact, then the measure of each angle formed is one half the measure of its intercepted arc.
Example:

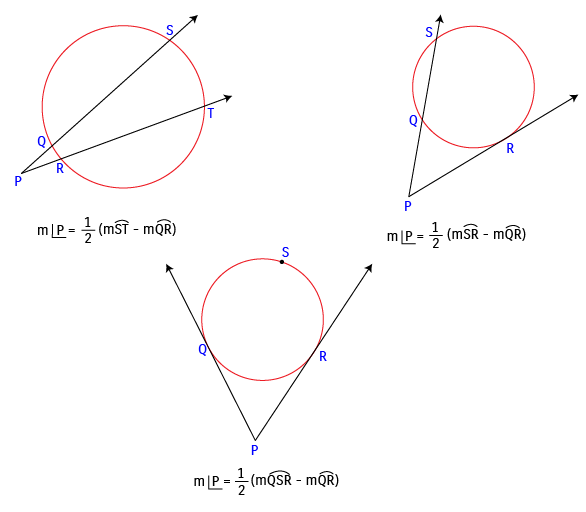
(iii) If two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersect in the exterior of a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is one half the positive difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
Example: