Calculating the number of enantiomers
Total no. of enantiomers = [No. of Stereoisomers] - [No. of diastereomers]
In general, number of diastereomers of a molecule is
calculated as 2n, where n is number of chiral centers in
the molecule (chiral carbon:asymmetric carbon that exhibits optical isomerism).
The relation holds true when the molecule does not have any meso forms (diastereomeric forms).
I. A molecule with one asymmetric carbon (stereocenter) forms
2 mirror images.
II. A molecule with two asymmetric carbons gives 4 configurations
that may or may not be mirror images of each other.
Examples:
Tartaric acid:
The acid has 2 asymmetric carbons that gives four possible configurations.
Among these, two isomers are meso type (optically inactive), while
the remaining are D - and L - isomers that are mirror images (enantiomers).
The possibilities continue to multiply with more asymmetric centers in a molecule.
A meso compound is an achiral compound that has chiral centers.
Although achiral compound has two or more stereocenters, it is optically inactive and
gives non-super imposable mirror images.
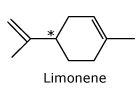
*An enantiomer has orange
smell while the other has lemon smell.
Carvone
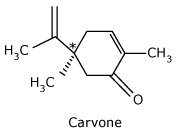
*(R) - Carvone is the
principal component of caraway seed oil and is responsible for its odor.
*(S) - Carvone
is the principal component of spearmint oil and is responsible for its odor.
Ibuprofen
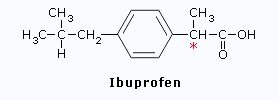
*In Ibuprofen, only the(S)
isomer is effective as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Therefore an enantiometrically pure
drug would work more effectively than a racemic mixture.
Thalidomide
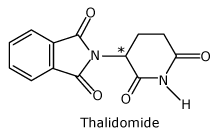
One of the enantiomers (the R form) alleviates morning sickness, the other is a potent mutagen that
causes birth
defects.
Pencillamine
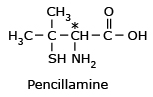
*(S) - Pencillamine is a potent drug
for chronic arthritis, whereas (R) - Pencillamine is not only useless for therapeutic
action, but is also highly toxic.
Methyldopa
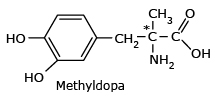 *Only the (S) isomer of methyldopa acts as antihypertensive drug; the other isomer has no
effect.
*Only the (S) isomer of methyldopa acts as antihypertensive drug; the other isomer has no
effect.
The complex nature of organic compounds - their tendency to form very
large molecules and their ability to occur as a wide variety of different types of isomers -
leads to the enormous variety of organic chemicals currently known to exist.