 Schrodinger's Cat
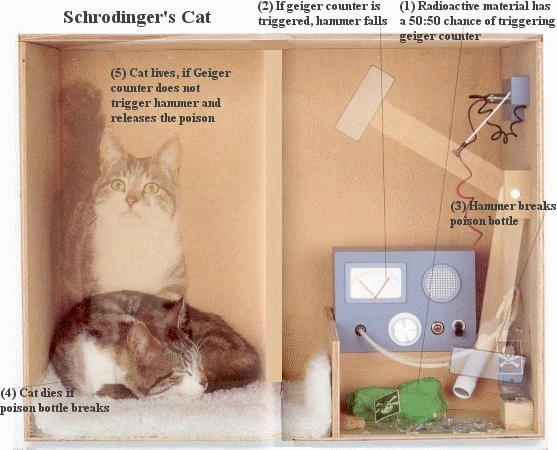
If an internal Geiger counter detects radiation, the flask is shattered, releasing the
poison that kills the cat. After a while, the cat is simultaneously alive and dead. Yet, when we look in the box,
we see the cat either alive (or) dead, not both alive and dead.
Schrodinger's Cat
If an internal Geiger counter detects radiation, the flask is shattered, releasing the
poison that kills the cat. After a while, the cat is simultaneously alive and dead. Yet, when we look in the box,
we see the cat either alive (or) dead, not both alive and dead.
Wave function is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves.
Probability amplitude is a complex number whose modulus squared represents a probability or probability density. The values taken by a normalized wave function Ψ at each point x are probability amplitudes.The properties of the wave function were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation was offered.
Schrodinger equation:The most general form of the Schrodinger equation is the time–dependent equation, which gives a description of a system evolving with time.
The time dependent schrodinger equation has a Hamiltonian operator which depends on time, where as the Time independent schrodinger equation too has a Hamiltonian operator which doesn't depend on time. One can easily calculate the Energy of the system using Time Independent schrodinger equation.