 Orbitals of Different Energy States:
Orbitals of Different Energy States:
The electron cloud model is an atom model wherein electrons are no longer depicted as particles moving around the nucleus in a fixed orbit.
There are a total of four quantum numbers; the principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml) and the electron spin quantum number (ms).
Principal Quantum Number ‘n’ :The principal quantum number n, describes the most probable distance of the electrons from the nucleus, n = 1, 2, 3, 4...... The Principal Quantum number ‘n’ cannot be zero or any negative integer, because there is no possibility to exists atoms with zero or a negative amount of energy levels/principal shells.
Orbital Angular Momentum Quantum Number ‘l’: The orbital angular momentum quantum number determines the shape of an orbital, and therefore the angular distribution. The value of l is dependent on the principal quantum number n. Unlike n, the value of l can be zero. It can also be a positive integer, but it cannot be larger than one and less than the principal quantum number (n − 1): For n = 3, l = 0, 1, 2......
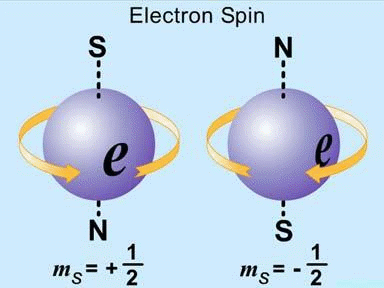 Electron spin:
Electron spin:
Magnetic Quantum Number ‘m’ :The magnetic quantum number ml determines the number of orbitals and their orientation within a sub–shell. Given a certain l, ml is an interval ranging from − l to + l.
Electron Spin Quantum Number ‘s’:Unlike n, l, and ml the electron spin quantum number ms does not depend on another quantum number. It designates the direction of the electron spin and may have a spin of +1/2, or −1/2.