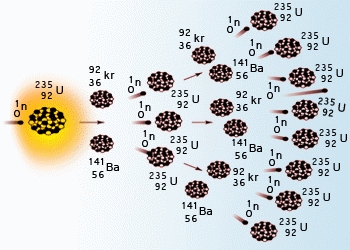
 Nuclear Chain Reaction using Uranium 235
For a chain reaction to be self-sustaining, the value of k must be greater than 1. Which implies that, the neutrons increase or multiply with time. If k = 1 then the condition is said to be critical.
Nuclear Chain Reaction using Uranium 235
For a chain reaction to be self-sustaining, the value of k must be greater than 1. Which implies that, the neutrons increase or multiply with time. If k = 1 then the condition is said to be critical.
It occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self–propagating number of these reactions.The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes (e.g. 235U) or the fusion of light isotopes (e.g. 2H and 3H). The nuclear chain reaction is unique since it releases several million times more energy per reaction.
When a single neutron initially causes the fission of 92U235 nucleus, 3 neutrons are released along with huge amount of energy. These 3 neutrons in turn cause three more nuclei to split, thereby liberating a total of 9 neutrons and so on. The process proceeds very quickly and in a very short time the whole of the uranium undergoes fission. A little reflection will show that for the fission to be self–sustaining, the number of emitted fission neutrons should be more than the incident ones. Under such conditions, the fission neutrons keep on increasing, thus maintaining the chain reaction. A very common term, called neutron multiplication factor (or reproduction factor), is often used in chain reactions.