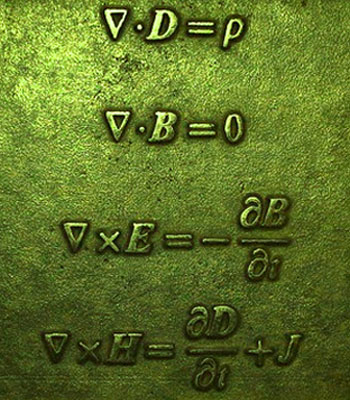 The four Maxwell's Equations that changed the world
The four Maxwell's Equations that changed the world
Maxwell's Equations:
A complete set of 4 equations that describe the theory of Electromagnetism.
These equations intensify the interaction of electric and magnetic fields with the
objects. Maxwell proved that the speed of propagation of light is same as the speed
of propagation of electromagnetic wave., which concludes that light is an Electromagnetic
wave.
A separated positive and negative charges give rise to an Electric field, which could vary with time leading to the propagation of the electric field, in turn giving rise to propagation of magnetic field. The first two equations of Maxwell are Gauss law for electric field and Gauss law for magnetism, which are used at constant voltages and currents.
The third and fourth equations are Faraday's law and Ampere's law which are the heart of electromagnetism. Faraday's law describe that the changing magnetic field produces a changing electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field. This means that the electric field changes as well. Ampere's law describe that the changing electric field produces a changing magnetic field perpendicular to it. This electric field will be changing with time.
Thus we can conclude that a changing magnetic field gives rise to a changing electric field and a changing electric field would give rise to a changing magnetic field, which itself will produce a changing electric field which would again give rise to another changing magnetic field and so on, this is known as the propagation of an Electromagnetic wave.
This propagation of an electromagnetic wave is possible even in vacuum, with out any medium. From the ampere's law and Faraday's law we can determine the speed of the electromagnetic wave.