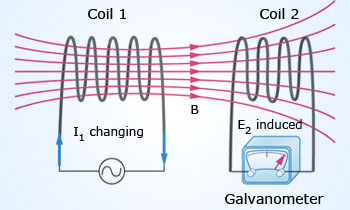
 Mutual Induction
As the current through the first coil changes continuously (AC) the emf is induced in the secondary coil
which is connected to a galvanometer.
Mutual Induction
As the current through the first coil changes continuously (AC) the emf is induced in the secondary coil
which is connected to a galvanometer.
Types of Inductions:
There are two types of Induction process: (1) Mutual Induction and (2) Self Induction.
(1) Mutual Induction: If suppose the current in the primary coil changes continuously, then the induced magnetic field of the primary coil produces a changing current in the secondary coil. One can even know what is the amount of current induced in the secondary coil. Also what is the amount of primary current is needed to produce an emf in the secondary coil.
The mutual inductance depends on several factor:
- Size and shape of circuits.
- No. of turns in each circuit.
- Distance between the circuits and
- Orientation of circuits.
If the current through a primary circuit is DC, it will not induce any emf in the secondary circuit and hence there will be no induced voltage.
 Self induction
Self induction occurs in inductor.
Self induction
Self induction occurs in inductor.
(2) Self Induction: Changing the current that is running through the same device induces the magnetic field, opposing the voltage in the same circuit. This opposing voltage acts just like a battery or a voltage source. The primary voltage source must do more work to perform some task.
Self induction depends on the geometry of the circuit. The straight wires have a small value of L, where as the looped coils will have large L.