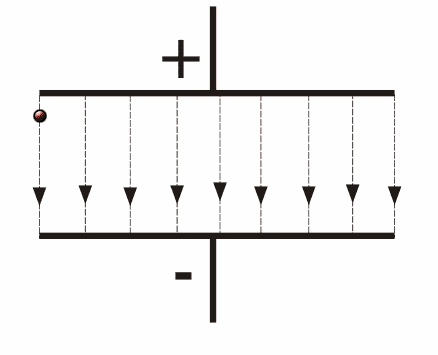
 Movement of a charged particle in a uniform electric field
If the Electric field is not strong then there will not be any deflection in the path of the charged particle while moving in a uniform electric field.
Movement of a charged particle in a uniform electric field
If the Electric field is not strong then there will not be any deflection in the path of the charged particle while moving in a uniform electric field.
Electrical potential V(t) of a position in the electrical field is such that, electric potential energy required to place a particle of charge q at that position would be the product of charge of the particle q and the potential of that position V(t). That is potential energy U(t) = q × V(t).
The SI unit of electrical potential is Volt after name of Italian physicist Alessandro Volta. Voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference between two points.
There is a misconception about potential and voltage. voltage is not exactly potential it is the measure of electric potential difference of two points.
Voltage is the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points. Voltage is the work to be done, upon an unit charge to move between two points, against a static electric field. A voltage which is a measure of electric potential difference is the cause of current to flow in a closed circuit.
Electrical Potential and Electrical Field vector both characterize the same thing that is space of electrical field. Since both electric potential and electrical field vector describe an electric field, they are related.
dV = –E.ds where dV is the potential difference between two points separated by a distance ds and electrical field vector is E.