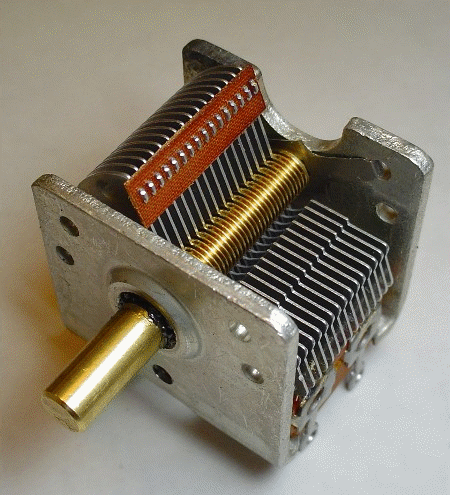
 Variable Capacitors
The air present between these plates acts as dielectric, which makes a variable capacitor, used in tuner circuits of Radios.
Variable Capacitors
The air present between these plates acts as dielectric, which makes a variable capacitor, used in tuner circuits of Radios.
An electrically insulating or nonconducting material considered for its electric susceptibility.
Dielectrics are insulating materials, they do not contain significant amounts of free charge, so charges on the plates of a capacitor that contain dielectrics still cannot pass from one side of the capacitor.
Capacitance of capacitor is increased by putting a dielectric material in between the conductor plates. It also allows a higher voltage across the capacitor than vacuum, and provides mechanical support. However, when a dielectric material is placed in an electric field it develops an electrical polarization. This can arise through several different physical mechanisms, for example, if the material has molecular dipoles they will orient themselves to line up with the field. Some crystals will develop electric dipoles in response to an electric field.
When a dielectric is used, the material between the parallel plates of the capacitor will polarize. The part near the positive end of the capacitor will have an excess of negative charge, and the part near the negative end of the capacitor will have an excess of positive charge. This redistribution of charge in the dielectric will thus create an electric field opposing the field created by the capacitor. Therefore, the net field created by the capacitor will be partially decreased, as the potential difference across it decreases, by the dielectric. On the other hand, the dielectric prevents the plates of the capacitor from coming into direct contact.