 Soap bubble
The beautiful colors from the surface of soap bubble can be nicely explained by the wave theory of light.
A soap bubble is a very thin spherical film filled with air, light reflected from the outer and inner surface of this thin film
of soapy water interferes constructively to produce the bright colors. The color we see at any point depends on the thickness of
the soapy water film at that point and also on the viewing angle.
Soap bubble
The beautiful colors from the surface of soap bubble can be nicely explained by the wave theory of light.
A soap bubble is a very thin spherical film filled with air, light reflected from the outer and inner surface of this thin film
of soapy water interferes constructively to produce the bright colors. The color we see at any point depends on the thickness of
the soapy water film at that point and also on the viewing angle.
First thing we can say about light is that it is something that enables us to see. But what is light? We know that during the day the primary source of the light is the Sun, and the secondary source is the brightness of the Sky. Other common sources are flames, white–hot filaments in light bulbs and glowing gas in glass tubes. Light is an electromagnetic phenomenon; visible light is a tiny part of a larger electromagnetic spectrum of radiation ranging from cosmic rays to radio waves. Knowledge of the nature of light and the emission and absorption processes are very important.
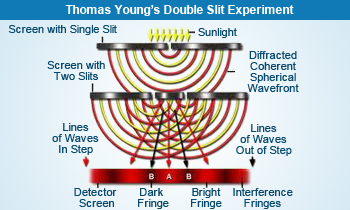 Thomas Young's Double Slit Experiment
Thomas Young's Double Slit Experiment
Two complimentary theories have been proposed to explain how light behaves and the form by which it travels.
- Particle theory: Release of small amount of energy as a photon when an atom is excited.
- Wave theory: Radiant energy travels as a wave from one point to another. Waves have electrical and magnetic properties (electromagnetic variations). Thomas Young conducted an experiment with two narrow slits inserted between the light source (laser) and the detector screen. Waves emerging from one slit are superimposed on waves from the other slit, producing the observed interference pattern with alternate dark and bright lines on the screen. Thomas Young's studies on diffraction and interference of light supported the wave theory of Christian Huygens's as opposed to the particle or corpuscular theory of Isaac Newton. Wave theory explained interference where the light intensity can be enhanced in some places and diminished in other places behind a screen with a slit or several slits. The wave theory is also able to account for diffraction where in the edges of a shadow are not quite sharp.
 Optical Fibers
These are the bundle of optical fibers that conduct light. These fibers are made of very pure glass which
is coated so as to allow light to be transmitted without absorption or loss of intensity. This allows data such as telephone
conversations, television pictures and computer transmissions to be sent in large volumes without loss of quality.
Optical Fibers
These are the bundle of optical fibers that conduct light. These fibers are made of very pure glass which
is coated so as to allow light to be transmitted without absorption or loss of intensity. This allows data such as telephone
conversations, television pictures and computer transmissions to be sent in large volumes without loss of quality.
Wave Particle Duality:
In 1923, Louis de Broglie, a French physicist, proposed a hypothesis frontiering the way to explain the theory of the atomic
structure. By using a series of substitution de Broglie hypothesizes particles to hold properties of waves. Within a few years,
de Broglie's hypothesis was tested by scientists shooting electrons and rays of lights through slits. What scientists
discovered was the electron stream acted the same was as light proving de Broglie correct.
Definition of Wave–Particle Duality
The behaviors of the electron does not allow for it to be observable as a particle and as a wave. The two sided nature of the
electron is known as the Wave–Particle Duality:The property of particles behaving as waves and the property of waves behaving
as particles as well as waves. Although the duality is not very effective in large matter. The wave characteristic of the electron
implicates many of the electron's particle behaviors.
Quantum Theory
Planck's Hypothesis of the Quantum Theory states that energy is emitted in quantas, little packets of energy, instead of a
continuous emission. He stated that energy emitted is related to the frequency of the light emitted. Planck's hypothesis
states that a quantum of energy was related to the frequency by his equation E = hv.
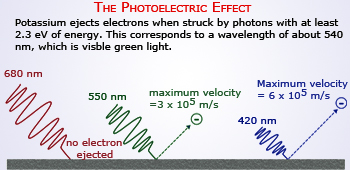 The Photoelectric Effect
The Photoelectric Effect
Waves and Particles Behaviors of Light (Photoelectric Effect)
An easy way to prove the duality between a particle and a wave is to observe light. At the time, many scientists believed that
light is a wave. Since light is like waves, it has the ability to diffract, reflect, refract, and interfere etc. Yet, light
behaved strangely at certain times, and scientists were befuddled until.
Albert Einstein's theory of photoelectric effect contributed greatly to De Broglie's Theory and was a proof that waves and particles could overlap. Light can also be observed as a particle known as photon. When light is shown on certain objects, the electrons will be released. Certain amounts of energy is needed to remove an electron from the surface of a substance. So, if a photon of greater energy than that of an electron hits a solid that electron will be emitted. However, scientists did discover that frequency of light effectively changed the amount of kinetic energy.