 The boat is less dense than water, hence it displaces a mass equal to its own instead of sinking.
The boat is less dense than water, hence it displaces a mass equal to its own instead of sinking.
Physical properties are those properties that can be measured or observed without changing the identity or composition of the substance. These properties can be sub categorized into intensive and extensive properties. Intensive properties are independent of the amount of the matter. Properties, such as, color, odor, melting point, boiling point, density, conductivity, malleability and ductility come under this category. Extensive properties will change with the change in the amount of the matter. Mass, volume, weight, length etc. are the examples of such properties.
Intensive properties:
1) Density:
Density is the mass per unit volume of a material:
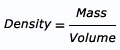
Less dense fluids float on more dense fluids. For example, the substances less dense than water, float and that are more dense,
sink. A piece of wood float on the surface of water whereas stone sinks in the water.
 Copper and Gold are both ductile and malleable metals, i.e., they can be rolled into thin sheets and can also
be stretched into wires.
Copper and Gold are both ductile and malleable metals, i.e., they can be rolled into thin sheets and can also
be stretched into wires.
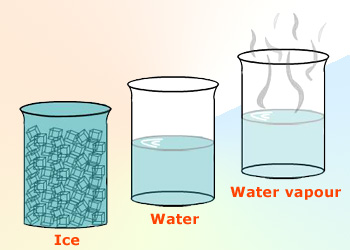 Three states of water are interconvertible. On heating liquid water evaporates and converts into vapor
whereas on cooling, it solidifies in the form of ice.
Three states of water are interconvertible. On heating liquid water evaporates and converts into vapor
whereas on cooling, it solidifies in the form of ice.
2) Malleability and ductility:
Malleability is the ability of matter to be hammered into thin sheets without breaking, while ductility is the ability of matter to be
stretched into wire.
3) Melting and Boiling points:
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes from solid to liquid state. It depends on the atmospheric
pressure. Boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which it changes from liquid to gas or vapor state. The melting and
boiling point of water are 0°C and 100°C respectively.
Extensive properties:
1) Mass and weight:
Mass is the measure of an object's inertia or the amount of matter in an object where as weight is the force experienced by an
object due to gravity. Mass remains constant and does not get affected by the force of gravitation, but weight changes with the
change in the gravity. As earth's gravity is about six times stronger than that of moon, therefore, a person's weight
on moon is less than his weight on the earth. The SI units of mass are kilogram (kg) and gram (gm). 1 gm is equal to the 1/1000 kg.
2) Length:
The longest dimension of an object is defined as its length. It can be measured in meter, centimeter, kilometer, decimeter etc.