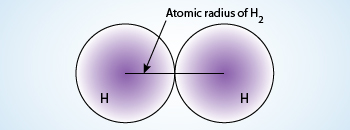
 Atomic Radius of hydrogen
Atomic Radius of hydrogen
All matter is made of small particles known as atoms. They are what make up the air, the water, our bodies, food. Atoms are made of three particles known at protons, neutrons and electrons. Unlike a ball the size of the atom has no boundaries. So, the size of the atom depends on whether the atom is losing an electron or gaining an electron.
The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of it's atoms, usually the distance from the nucleus to the outer shell electrons (valence electrons). In simpler terms, it can be defined as something similar to the radius of a circle, where the center of circle is nucleus and the outer edge of the circle is the outermost orbital of electron.
 Example showing van der waal's radii
Example showing van der waal's radii
Van der waals radius :
It is half the minimum distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the element that are not bound to the same molecule.
Ionic Radius :
The ionic radius is the radius of an atom forming ionic bond or an ion. The radius of each atom in an ionic bond will be
different due to the fact that the atoms in ionic bond are of greatly different sizes.
When we compare the size of cation, as we all know the positively charged ion to the neutral atom of the same element. The neutral atom shows more bond length compared to cation because of lose of electrons consequently result in change in atomic radii. This will cause a decrease in atomic size because now there are fewer electrons which will result in stronger pull of electrons towards the nucleus.
An analogy is that, in a class room of 10 students a teacher can concentrate well, here the teacher is compared to nucleus and students as electrons. As the number of students decreases the concentration of teacher on each student increases, the students are pulled or dragged by the concentration of a teacher so the electrons are pulled by the nucleus and size of the cation decreases.
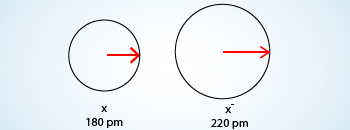 Comparison of radii of neutral atom with radii of Anion
Comparison of radii of neutral atom with radii of Anion
Comparison of size of Cation with its neutral atom:
Anion as we know already that it is formed from its atom by gain of electrons. The gain of electrons to the outermost shell which
increases the radius because there are now more electrons further away from the nucleus so the pull becomes slightly weaker than
neutral atom and causes increase in atomic radius.
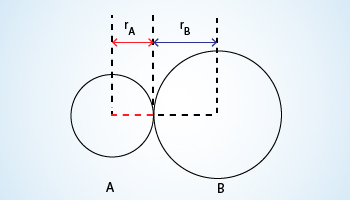 R = rA + rB (R is the bond length and rA and rB are the covalent
radii of atoms A and B respectively).
R = rA + rB (R is the bond length and rA and rB are the covalent
radii of atoms A and B respectively).
Covalent radii:
Covalent radius can be determined in molecules where atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, the radius of each atom will be half the
distance between the two nucleii because they equally attract the electrons.The distance between the nuclei give the diameter
of the atom, but we want the radius which is half the diameter