 Nuclear fission reaction
Nuclear fission produced as a result on bombardment of neutron with the heavy nucleus. This results in the
production of energy at every step and the other fission producing neutrons, leading to the production in enormous amounts of
energy.
Nuclear fission reaction
Nuclear fission produced as a result on bombardment of neutron with the heavy nucleus. This results in the
production of energy at every step and the other fission producing neutrons, leading to the production in enormous amounts of
energy.
Mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. Just as atoms can react chemically to produce newer molecules, nuclei can react to produce newer nucleus.
These nuclear combinations are known as nuclear reactions. Small mass nuclei fuse together to form another nuclei – this reaction is known as fusion reaction. Whereas large nuclei can break up, even spontaneously, to form smaller nuclei – this reaction is known as nuclear fission reaction.
Nuclear Fission:
When uranium–235 atoms are bombarded with slow moving neutrons, the heavy uranium nucleus breaks up to produce two
medium–weight atoms – Barium139 and krypton–94, with the emission of neutrons. A great amount of energy is
produced during the fission of uranium. The fission reaction can be represented in the form of a nuclear equation as:
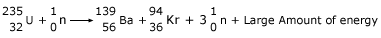
Heavy atom + Neutron ⟶ Medium weight atoms + Neutrons + large energy.
Nuclear fission of a heavy atom by slow moving neutrons produces:
- Two medium weight nuclei (or two medium weight atoms)
- Three neutrons (or in some cases two neutrons)
- Radiations of very short wavelength called gamma rays (which is similar to X–rays), and
- Enormous amount of heat and light energy.
 Critical nuclear fission
Critical nuclear fission is a controlled fission reaction in which the number of neutrons producing fission
are controlled by the readily control rods which permit only required number of neutrons to produce the heat at a constant rate.
Critical nuclear fission
Critical nuclear fission is a controlled fission reaction in which the number of neutrons producing fission
are controlled by the readily control rods which permit only required number of neutrons to produce the heat at a constant rate.
Fission Reactions:
Nuclear fission reaction is of two types:
- Explosive fission reaction (or uncontrolled fission reaction)
- Critical fission reaction (or controlled fission reaction).
Explosive fission reaction (or uncontrolled fission reaction):
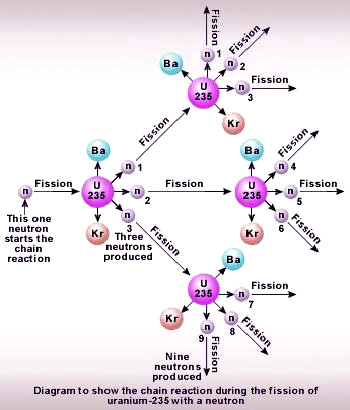
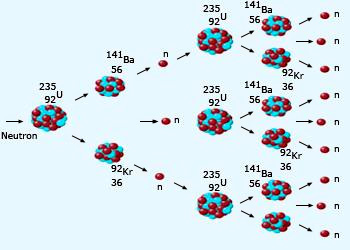
When a slow moving neutron hits the nucleus of a uranium–235 atom, then the nucleus of uranium–235 atom undergoes
fission, producing barium nucleus, krypton nucleus and 3 neutrons, along with a lot of energy. Now, if we have a considerable
quantity of uranium–235 atoms, then the 3 neutrons produced by the fission of first U–235 atom would cause the
fission of 3 more uranium atoms, producing 3 × 3 = 9 neutrons, and a lot more energy. These 9 neutrons can cause the
rupture of 9 more uranium atoms, giving out 9 × 3 = 27 neutrons, and yet more energy. This process of fission of
uranium–235 atoms, production of more neutrons and release of more and more of energy goes on multiplying endlessly. This
is known as the chain reaction.
Critical fission reaction:
A critical fission reaction is that fission reaction in which each fission of uranium–235 is allowed to retain just enough
neutrons to ensure that the number of uranium atoms undergoing fission remains constant with time and does not go on multiplying
endlessly. When a fission reaction becomes critical, we say the “criticality” has been achieved. In most simple terms,
a critic fission reaction means a controlled fission reaction, that is, a fission reaction that produces energy at a slow, steady
and manageable rate.