Accuracy
Structure of Matter > Chemical Calculations
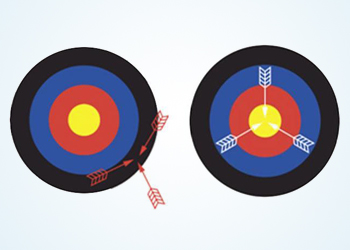
- In first case the arrows are pointed with poor accuracy.
- In second case the arrows are pointed with good accuracy.
It is the degree of agreement between the experimental value and accepted true value.
The accuracy of a result is effected by the systematic errors. The accuracy of the result is determined by the following two methods:
- Absolute method: In this method, a sample containing known amounts of constituents is taken by weighing a pure compound of known stoichiometric composition. The accuracy of the method is determined by the difference between the mean of number of results obtained and the amount of the constituent actually present, usually expressed in parts per thousand.
- Comparative method: This method involves secondary standards. If a sample can be analyzed by different methods like gravimetry, titrimetry, spectrophotometry etc. The result in close proximity with at least two methods is considered.
- Accuracy is how close to a true value the given measurement is.