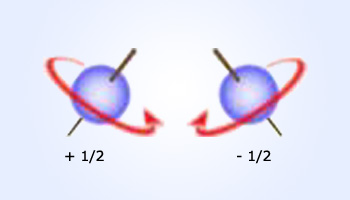
 Electrons behave in certain respects as if they were tiny charged spheres spinning around an axis. This
gives rise to a tiny magnetic field to the fourth quantum number,ms, which have a value of +1/2 and −1/2.
Electrons behave in certain respects as if they were tiny charged spheres spinning around an axis. This
gives rise to a tiny magnetic field to the fourth quantum number,ms, which have a value of +1/2 and −1/2.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. We are aware that in
one orbital a maximum of two electrons can be found and the two electrons must have opposing spins. That means one would
spin up ( +1/2) and the other would spin down (−1/2)
Example :

We have the first three quantum numbers n=1, l=0, ml=0. Only two electrons can correspond to these, which would be either ms = −1/2 or ms = +1/2. As we already know from our studies of quantum numbers and electron orbitals, we can conclude that these four quantum numbers refer to 1s sub shell. If only one of the ms values are given then we would have 1s1 (denoting Hydrogen) if both are given we would have 1s2 (denoting Helium). Visually this would be represented as in the picture shown beside.