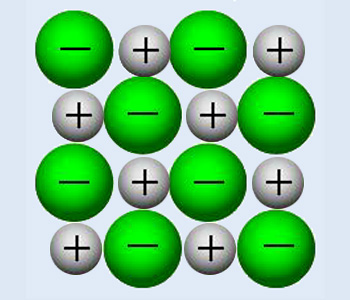
 Ionic Bond
Ionic Bond
Do you know the fact why mars is red? Mars is red because its surface contains a lot of iron oxide or rust. The rust formed is iron oxide which is formed by the reaction of iron with oxygen.
Chemical reactions takes place around us in day to day life. Scientists would not be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how the products are formed after the chemical reactions has taken place without our fundamental topic Chemical bonding. Bonding takes place in different ways, one of it is Ionic Bonding.
Ionic Bond:
The electrostatic bond between two ions formed through the transfer of one or more electrons is called Ionic Bond.
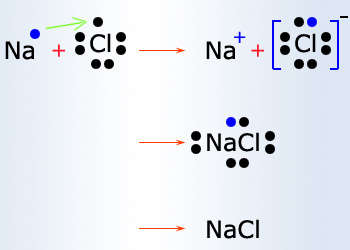
Electrostatic Bond:
The chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion and another atom gains an electron to form a negative
ion.
Ionic bond is observed because metals have few electrons in its outer most orbital. By losing those electrons,
these metals can achieve noble gas configuration and satisfy the octet rule. Similarly, non–metals that have close to 8
electrons in its valence shell tend to readily accept electrons to achieve its noble gas configuration.
The charge on the anion or cation corresponds to the number of electrons donated or received. In ionic bonds the net charge of
the compound must be zero.
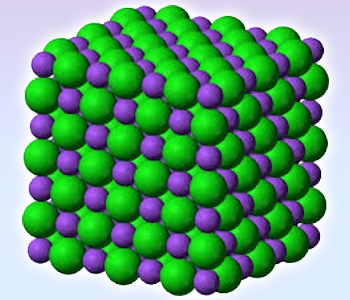 Sodium chloride – Hexagonal close packing
Sodium chloride – Hexagonal close packing
Properties of Ionic compounds:
1. Ionic compounds form crystal lattice.
Crystal lattice: The arrangement of atoms, molecules or ions of a crystal in the form of a space lattice.
Examples: Sodium chloride : Hexagonal close packing
Caesium chloride : cubical close packing
In sodium chloride, each ion is surrounded by six ions of opposite charge as expected on electrostatic grounds. The surrounding ions are located at the vertices of a regular octahedron. The larger chloride ions are arranged in a cubic array where as smaller sodium ions fill all the cubic gaps between them.
2. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points: In ionic compounds the force of attraction between positive and negative ions are so strong, so need high temperatures to overcome them.
3. Ionic compounds are hard and brittle: Ionic crystals are hard because the positive ions and negative ions are strongly attracted to each other and difficult to separate. When pressure is applied to an ionic crystal the ions of like charge may be forced closer to each other. The electrostatic repulsion can be enough to split the crystal, which is why ionic solids are brittle.