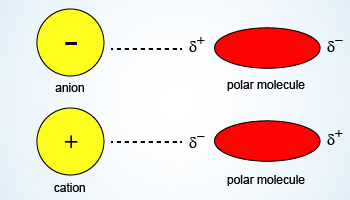
 Image Showing Ion–dipole Forces
Ion–dipole attractions become stronger as either the charge on the ion increases, or as the magnitude of the dipole of the polar molecule increases.
Image Showing Ion–dipole Forces
Ion–dipole attractions become stronger as either the charge on the ion increases, or as the magnitude of the dipole of the polar molecule increases.
Forces binding atoms in a molecule are due to chemical bonding. The forces holding molecules together are generally called intermolecular forces.
Ion–dipole force:
- An ion–dipole force is an attractive force that results from the electrostatic attraction between an ion and a neutral molecule that has a dipole.
- Most commonly found in solutions. Especially important for solutions of ionic compounds in polar liquids.
- A positive ion (cation) attracts the partially negative end of a neutral polar molecule.
- A negative ion (anion) attracts the partially positive end of a neutral polar molecule.
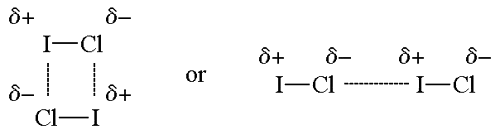 Dipole–dipole Forces
The partially positive iodine end of one ICl molecule is attracted to the partially negative chlorine end of another ICl molecule.
Dipole–dipole Forces
The partially positive iodine end of one ICl molecule is attracted to the partially negative chlorine end of another ICl molecule.
Dipole–dipole forces:
- Dipole–dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
- Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end.
- The partially positive end of a polar molecule is attracted to the partially negative end of another.
- In a ICl molecule the more electronegative chlorine atom bears the partial negative charge; the less electronegative iodine atom bears the partial positive charge.
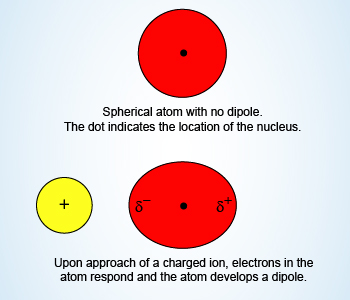 Example Showing Ion–Induced Dipole Forces
Example Showing Ion–Induced Dipole Forces
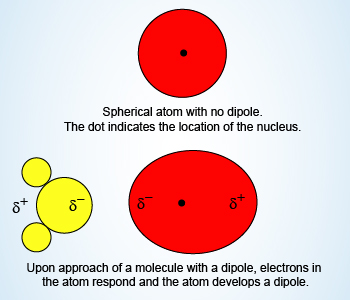 Example Showing Dipole–Induced Dipole Forces
Example Showing Dipole–Induced Dipole Forces
Induced dipole forces result when an ion or a dipole induces a dipole in an atom or a molecule with no dipole. These are weak forces.
- Ion–Induced Dipole Forces
- Dipole–Induced Dipole Forces
Ion–Induced Dipole Forces:
An ion–induced dipole attraction is a weak attraction that results when the
approach of an ion induces a dipole in an atom or in a nonpolar molecule by
disturbing the arrangement of electrons in the nonpolar species.
Dipole–Induced Dipole Forces:
A dipole–induced dipole attraction is a weak attraction that results
when a polar molecule induces a dipole in an atom or in a nonpolar
molecule by disturbing the arrangement of electrons in the nonpolar species.