 Polluted water
Polluted water
Water pollution is the action of environmental contamination with man made waste into water bodies such as lakes, rivers, oceans and groundwater. Although natural phenomena such as volcanoes, algae blooms, storms and earthquakes also cause major changes in water quality and the ecological status of water, water is only called polluted when it is not able to be used for what one wants it to be used for. Water pollution is a major problem in the global context. It has been suggested that it is the leading worldwide cause of deaths and diseases and that it accounts for the deaths of more than 14,000 people daily.
Water pollution has many causes and characteristics. Organic wastes such as sewage impose high oxygen demands on the receiving water leading to oxygen depletion with potentially severe impacts on the whole ecosystem. Industries discharge a variety of pollutants in their wastewater including heavy metals, resin pellets, organic toxins, oils, nutrients and solids. Discharges can also have thermal effects, especially those from power stations and these too reduce the available oxygen. Silt–bearing runoff from many activities including construction sites, deforestation and agriculture can inhibit the penetration of sunlight through the water column, restricting photosynthesis and causing blanketing of the lake or river bed, in turn damaging ecological systems.
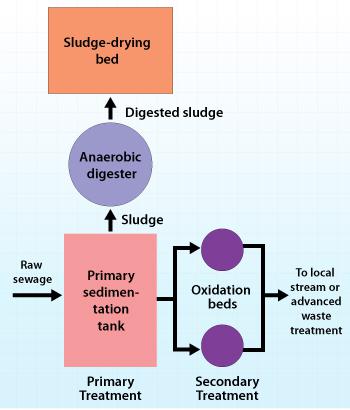 Sewage water treatment
Sewage water treatment
Water pollution can arise from either point sources or non–point sources.
- A point source is one, specific, well defined location where a pollutant enters a body of water. Point source emits harmful substances directly into a body of water. Example of a point source would be the out falls from wastewater pipes of a factory or sewage treatment plant, refineries, many organic and inorganic substances including human waste and toxic metals etc.
- A non–point source delivers pollutants indirectly through environmental changes. Majority of contamination is due to non–point sources. Non–point source pollution mainly caused by runoff, when rain move over the land, picking up the pollutants along the way and dumping the pollutants into the rivers and lakes.
Municipal solid waste disposal sites are a common source of groundwater pollution. Rainwater infiltrating a disposal site may dissolve a variety of chemicals from the solid waste. The resulting solution, known as leachate, can move into the groundwater, forming a contamination plume that spreads in the direction of groundwater flow.
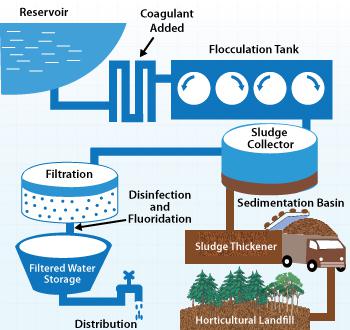 Water purification plant
Water purification plant
Water Treatment:
Water is the most important nutrient in our diets. A human adult requires approximately 2 liters of water every day to replenish
the water that is lost from the body through the skin, respiratory tract and urine. Though the water in rivers, lakes and
underground sources is fresh water, it can't be used directly for drinking because water may contain many dissolved species
like:
- Ions (e.g., Na+, Ca2+, F−, and HSO4−)
- Dissolved gases (e.g., O2 and CO2)
- Other natural dissolved molecules (e.g., organic by – products of decaying leaves)
- Dissolved molecules from human activity (e.g., industrial and agricultural wastes)
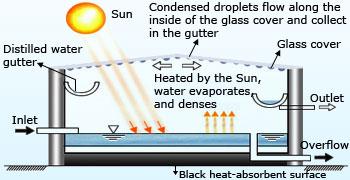 Solar desalination process
Solar desalination process
Desalination:
In regions where the availability of fresh water is limited, there has been growing interest in techniques capable of generating
fresh water from the Earth's far larger reserves of seawater or from brackish (moderately salty) groundwater. Desalination
or desalinization refers to any of several processes that remove excess salt and other minerals from seawater or brackish water.
Desalination processes are of two types, thermal processes and membrane processes. Thermal processes involve
heating of water to produce water vapor and membrane processes involves the use of permeable membranes for the movement of water
molecules to produce fresh water.
A number of methods have been developed for desalination including electro dialysis, distillation, reverse osmosis, vacuum
freezing, solar humidification etc. Out of these methods reverse osmosis (which is a membrane process) and multistage flash
distillation (which is a thermal process) are being considered for seawater distillation.
Electro dialysis method of desalination involves the usage of membranes to filter out the excess salts present in the water in the form of positively and negatively charged salt ions.
Distillation method involves heating of salt water to make it to evaporate leaving the salts behind, and the vapors are condensed into a container to get fresh water.
Solar desalination:
In solar desalination process, solar energy was employed for the desalination of water. Solar – distillers avoid the
burning of fuels but require about 1 square meter of surface area to produce 4 liters of fresh water per day. For a single
home or small village, this surface area requirement may be easily accommodated.
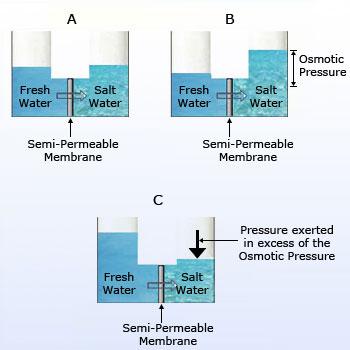 Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis
 Multistage flash distillation
Multistage flash distillation
Reverse osmosis:
Reverse osmosis is exactly reverse to the osmosis. Osmosis is a process in which there is a net flow of water molecules from
high concentration of water molecules to low concentration of water molecules separated by a semipermeable membrane.
Semipermeable membrane is a membrane, which consists of submicroscopic pores that allows the passage of solvent molecules.
Osmosis can be slowed, stopped, or even reversed if sufficient pressure is applied to the membrane from the ‘concentrated’
side of the membrane.
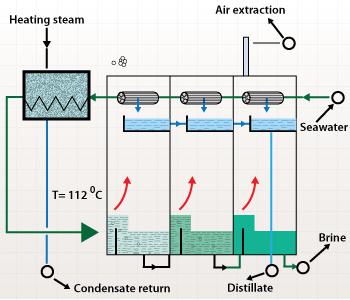
Multistage flash distillation:
Multistage flash distillation is another widely used technique for desalination of salt water. The process involves boiling of
salt water to high temperatures by passing water into a steam of multiple stages to make it to evaporate, leaving the salts
behind and then condensing these vapors by passing through vessels containing decreased pressure to get fresh water. Reverse
osmosis plants are the most common type, but multistage flash distillation plants produce over 85 percent of all desalinated
water in the world.