 Soil pollution
Soil pollution
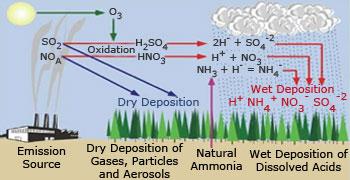 Soil pollution by various methods
Soil pollution by various methods
Soil is a thin covering over the land consisting of a mixture of minerals, organic material, living organisms, air and water, that together support the growth of plant life. In general, soil pollution/soil contamination is defined as the presence of toxic chemicals (pollutants or contaminants) in soil in high enough concentrations to be of risk to human health and ecosystem.
All soils whether it is polluted or unpolluted contains a wide variety of compounds/contaminants which are naturally present. Phosphates, carbonates, sulphates, nitrates and many other organic compounds like lipids, proteins, DNA, fatty acids, hydrocarbons, PAHs, alcohols etc., are the some of the contaminants which are naturally present in the soil. These compounds are mainly formed through soil microbial activity and decomposition of organisms like plants and animals.
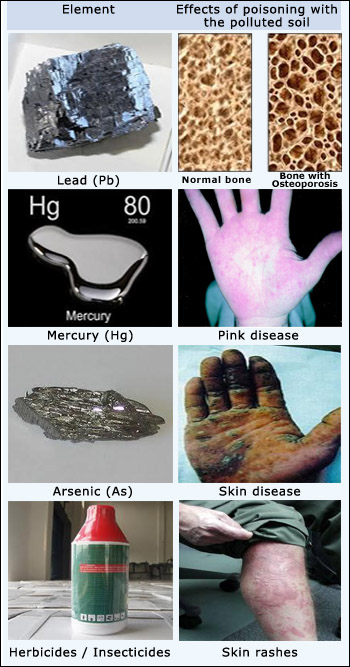
Some Soil Pollutants:
Lead (Pb):
Source: Lead paint, mining, foundry activities, vehicle exhaust
Effects of poisoning with the polluted soil:
- Affects the nervous system and memory, growth and development, as well as cognitive development (lower Iqs).
- Autism in genetically predisposed people,growth reduction and weight loss, impair pituitary-thyroid endocrine system.
Mercury (Hg):
Source: Mining, incineration of coal, alkali and metal processing, medical and other waste volcanoes and geologic deposits.
Effects of poisoning with the polluted soil:
- High blood pressure and hypersalivation,tachycardia.
- Loss of hair, teeth, nails, photophobia, kidney disfunction, memory impairment, insomnia – in children.
Arsenic(As):
Sources: Mining, coal–fired power plants, lumber facilities (used as CCA – chromate copper arsenate in pressure treated wood), electronic industry, foundry activities, agriculture (pesticides – including some of those currently used), natural accumulation under specific conditions.
Effects of poisoning with the polluted soil:
- If ingested –the most specific effects relates to skin pattern changes and cancer (including liver, kidney, bladder, prostate and lung cancer).
- If inhaled – skin changes; irritation of throat and lungs, circulatory problems, nervous system disorders.
Herbicides/Insecticides:
Souces: Agricultural activities, Gardening
 Rivers carry numerous water borne diseases like cholera.
Rivers carry numerous water borne diseases like cholera.
Effects of poisoning with the polluted soil:
- Large range of effects from skin rashes to death.
Diseases caused due to soil pollution: Soil pollution may cause a variety of health problems starting with headaches, nausea, fatigue, skin rash and/or eye irritation and potentially resulting in more serious conditions, of which, the most common soil pollution diseases include:
- Cancer: Benzene, weed killers, pesticides, chromium, are carcinogenic agents. The exposure to these agents causes cancer. The prolonged exposure to benzene may lead to leukaemia and irregular menstrual problems in women and anaemia. A high level of exposure to benzene is fatal.
- Kidney and liver disease: Lead exposure from soil also puts people at risk for kidney damage. Exposure to soil contaminated with a combination of mercury and cyclodienes increases the risk of developing incurable kidney damage. Exposure to PCBs and cyclodienes may cause liver toxicity as well.
- Brain and nerve damage: Mostly the brain and nerve damage can be seen in the children who are mostly exposed to the harmful effects of soil polluted areas like playground and parks, where lead–contaminated soil has been proven to cause brain and neuromuscular development problems.
- Malaria: The people living in the tropics, where the rainfall is heavy, are most prone to malaria. Contaminated water or raw sewage may mix with soil in these tropics. The protozoa that causes malaria and the mosquitoes that act as carriers thrive in such conditions; the resulting increased propagation of both the protozoa and the mosquitoes leads to frequent outbreaks of malaria.
- Cholera and dysentery: Soil pollution is closely linked to water pollution, because when the soil is contaminated, it leaches into surface and ground water, leading to the contamination of drinking water and an outbreak of water–borne diseases like cholera and dysentery.