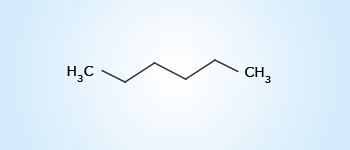
 Hexane
Hexane According to IUPAC system, the systematic name of the organic compound consists of three parts :
- Root word
- Suffix
- Prefix
1) Root word:
A root word indicates the nature of the basic carbon skeleton. For chains
containing upto four carbon atoms special root words are used and for those with more than four carbon atoms, Greek numerals are
used.
Eg: Meth–, Eth –, Prop –, but –, Pent – so on
2) Suffix :
The root word is linked to the suffix. Suffix may be primary suffix and secondary suffix.
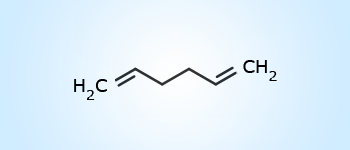 1,5–hexadiene
1,5–hexadiene Primary suffix:
Primary suffix indicates the degree of saturation(single bond) or unsaturation (double or triple bond) in the carbon chain.
For single bonded carbon atoms, the primary suffix is “ ane”. For the double bonded carbon atoms,
it is “ene” and for the triple bonded carbon atoms, the primary suffix is “yne” .
If the parent chain contains two, three or more double or triple bonds, then the following suffixes are used:
Two double bonds – diene; Three double bonds – triene:
Two triple bonds – diyne; Three triple bonds – triyne.
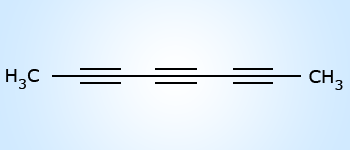 Octa‐2–4–6–triyne
Octa‐2–4–6–triyne Secondary suffix:
Secondary suffix indicates the functional group present in the molecule. It is added after the primary suffix. Depending on the
number of occurrences of the same functional group in a compound, the words like di, tri, tetra etc., are prefixed to the
secondary suffix.
While adding the secondary suffix to the primary suffix, the terminal ‘e’ of the primary suffix
(i.e., ane, ene or yne) is dropped if the complete secondary suffix (di, tri,
tetra etc., (if any) + secondary suffix) begins with a vowel. However, the terminal ‘e’ is retained
if the complete secondary suffix begins with a consonant.
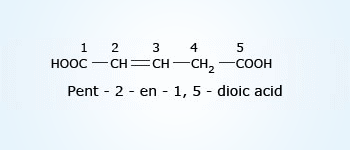
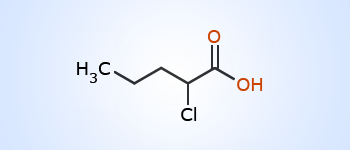 2–chloropentanoicacid
2–chloropentanoicacid When an organic compound contains two or more functional groups, one group is treated as the principal
functional group and is regarded as secondary suffix whereas the other functional groups are regarded as substituent and are
indicated by prefixes.
The order for the preference of principal functional group is as given below:
sulphonic acids > carboxylicacid > acidanhydrides > esters > acyl halides > amides > aldehydes > nitriles >
acetones > alcohols > amines > ethers.
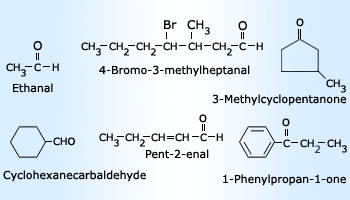 Number prefix nomenclature
Number prefix nomenclature 3) Prefix:
Prefix is a word written in front of a root word. Primary prefix and secondary prefix are two types of prefixes.
- Primary prefix:
For cyclo alkanes the word ‘cyclo’ is used as a prefix of root word to indicate that it is a ring compound. - Secondary prefix:
It is further classified in to two types as word prefix and number prefix. - Word prefix:
It indicates the substitution of other groups (not regarded as functional groups) in place of hydrogen atoms in the compound. These are regarded as substituents or side chains and the names of these are prefixed to the root word in alphabetical order. These names may be Alkyl groups (formed by the removal of hydrogen atom from alkanes. Some functional groups which are not considered as principal functional groups. - Number prefix:
It is used to indicate the multiplicity of a substitute or side chain in the given compound.