
Nucleic acids are the molecules that preserve hereditary information and transcribe and translate it to synthesize various types of proteins.
The first nucleic acid wad isolated from the nucleus and hence got this name. These molecules are sometimes found in association with proteins, and therefore, are called nucleoproteins. The monomeric unit of nucleic acids is called nucleiotide and is comprised of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base (purine or pyramidine), and a phosphoric acid. Two types of nitraogenous bases are present in nucleic acids, purines, e.g., adenine and guanine; pyramidines, e.g., cytosine, thymine and uracil.
The heterocyclic base of a nucleotide is attached to the C1' of ribose or deoxyribose unit and the phosphate group is attached at the C5' or C3' position.
There are two classes of nucleic acids:
1.Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
2.Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
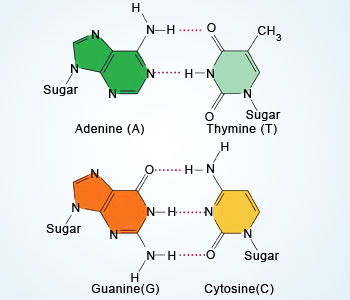
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): DNA encodes the genetic information and trasmit it from one generation to another and thus maintains the integrity of a living species. It is a self replicatory molecule. The DNA is composed of nucleotides, each containing one of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine; one molecule of deoxribose sugar, and a phosphate group. Watson and Crick proposed the double–stranded helical structure of DNA which states that DNA contains two polynucleotide chains coiled around each other and linked together through hydrogen bonds between the bases. Adenine binds with thymine via two hydrogen bonds, whereas guanine binds with cytosine via three hydrogen bonds. The two strands of DNA are complementary to each other.
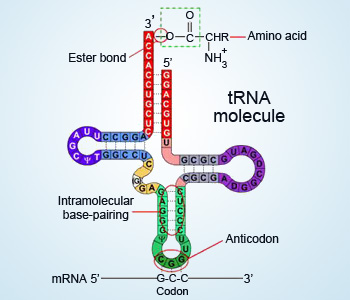
Ribonucleic acid (RNA): RNA molecules are also composed of sugar–phosphate backbone and four types of bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. The pentose sugar found in RNA is ribose sugar. The three main types of RNA are enlisted below:
- mRNA: It carries genetic information from DNA to ribosome where protein synthesis takes place.
- rRNA: These molecules are the integral part of ribosomes and also take part in protein synthesis.
- tRNA: These molecules act as a carriers of amino acids and tranfer them to the ribosome where protein synthesis occurs. It is covalently attached to the corresponding amino acid at one end and to the triplet anticodon sequence on the other end. This anticodon sequence is complementary to the triplet codon in the mRNA.
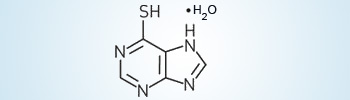 6–Mercaptopurine
6–Mercaptopurine
Medical applications:
In the early 1950's, Elion and Hitchings discovered that 6–mercaptopurine (a purine derivative) had antitumor and antileukemic properties. This drug is used in combination with other therapeutic agents to treat acute leukemia in children. Since then, many other purine based drugs have been developed to treat cancer and viral infections.