 Red Phosphorus
Red Phosphorus
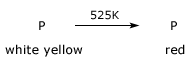
It is less reactive form of phosphorus. It is obtained by heating white phosphorus in a closed iron retort
in an inert atmosphere at 525K for several hours. A trace of iodine accelerates the transformation of white into red variety and
it takes place rapidly at much lower temperature. Unchanged white phosphorus is removed by dissolving in caustic soda.
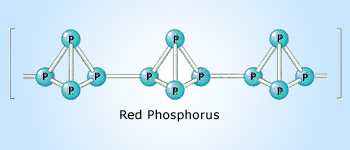 Red phosphorus polymeric structure
Red phosphorus polymeric structure
Structure
Red phosphorus has polymeric structure in which many P4 tetrahedra are joined to each other by covalent bonds.
Due to the polymeric structure in which different tetrahedra are held together by relatively stronger covalent bonds, red phosphorus is thus less volatile, less soluble in CS2 and less reactive than white phosphorus because of its polymeric structure.
 Burning of Red Phosphorus
Burning of Red Phosphorus
Properties of red phosphorus
- It is a dark red powder with density 2.1
- It is odorless and non–poisonous
- It is insoluble in water as well as in carbon disulfide
- It sublimes on heating to about 565K in absence of air.
- Its ignition temperature (553K) is quite high. Hence there is no need to store it under water.
- It is converted into white variety when boiled in an inert atmosphere and the vapors condensed under water.
- It does not glow in the dark.
- It does not react with caustic soda.
- It burns to given P4O10 when heated above 533K .
- It combines with halogens, sulphur and metals only when heated.