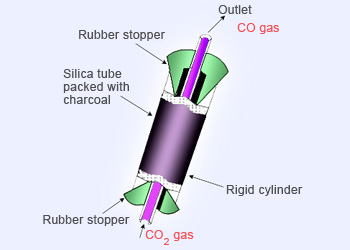
 Reduction of carbon dioxide with charcoal.
Reduction of carbon dioxide with charcoal.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
It is an oxide of carbon found in small amounts in volcanic gases, chimney gases, exhaust gas of internal combustion engines
and coal gas. Carbon monoxide is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon or carbon containing fuels.

Bond structure of CO
CO Has 14 electrons, is isoelectronic with nitrogen (N2). It has the highest bond enthalpy (1070 kJ mol−1)
among diatomic molecules. A molecular orbital description suggests the presence of a triple bond between carbon and oxygen.
CO is a resonance hybrid of the structures given below.
Electronic structure of carbon monoxide

 Preparation of carbon monoxide from farmic acid
Preparation of carbon monoxide from farmic acid
Preparation methods of CO
By the reduction of carbon dioxide with coke
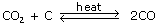
By the reduction of carbon dioxide with zinc or iron.

By the reduction of oxides of heavy metals with carbon.

In laboratory CO is produced by heating formic acid with sulphuric acid. This method gives pure CO.

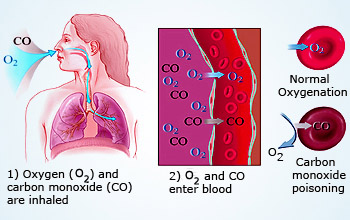 Carbon monoxide poisoning of blood
Carbon monoxide poisoning of blood
Properties of CO
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless and a poisonous gas.
Carbon monoxide reacts with the hemoglobin in the red blood cells to form carboxy hemoglobin. Carboxy hemoglobin is not able to carry oxygen. This causes deficiency of oxygen in the body, resulting into suffocation and even death.
 CO chemical properties
CO chemical properties
Carbon monoxide is combustible but a non–supporter of combustion. Carbon monoxide burns in air with a pale–blue flame giving carbon dioxide.

- It acts as a reducing agent ,reduces many metal oxides to the metals and also reduces I2O5 to iodine.
- Carbon monoxide forms methyl alcohol on reaction with hydrogen in presence of catalyst at suitable temperature and pressure.
- CO forms phosgene on reaction with chlorine. Phosgene was used as a chemical weapon in world war 1.
- CO under suitable pressures react with sodium hydroxide forms sodium formate.
- Carbon monoxide combines with many transition metals under suitable conditions to form carbonyls.
 Mond balls
These pure nickel balls are produced by the mond process
Mond balls
These pure nickel balls are produced by the mond process
Uses of Carbon monoxide
- CO is used as a fuel in the form of producer gas or water gas.
- It is used in production of chemical products such as aldehydes and acetic acid.

Producer gas is obtained by passing air over red hot coke at 1300
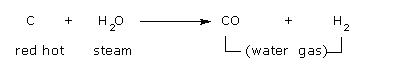
Water gas is obtained by passing steam over hot coke
- In the metallurgy of nickel for the purification of nickel by Mond's process.
- In the manufacture of methanol and synthetic petrol.
- In the manufacture of phosgene used in dye industry and warfare.