 Silver is reduced and Copper is oxidized
Silver is reduced and Copper is oxidized
A reducing agent, or reductant, loses electrons and is oxidized in a chemical reaction. A reducing agent typically is in one of its lower possible oxidation states and is known as the electron donor. A reducing agent is oxidized because it loses electrons in the redox reaction. Examples of reducing agents include the earth metals, formic acid and sulfite compounds.
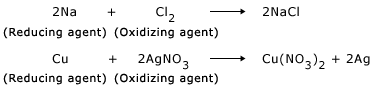
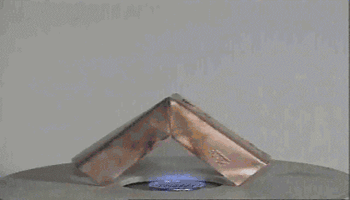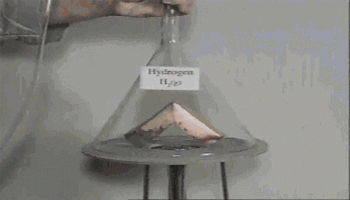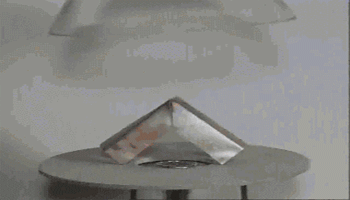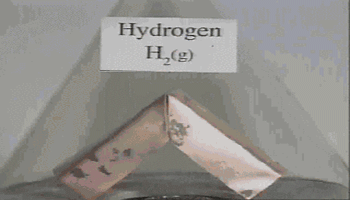 Action of hydrogen on copper oxide
Action of hydrogen on copper oxide

CuO is an oxidizing agent and H2 is a reducing agent

Here H2S is a reducing agent and Cl2 is an oxidizing agent.
Oxidizing and reducing agents are routinely used for extraction of metals and non–metals from ores. Also these reactions are seen in all storage cells or batteries.