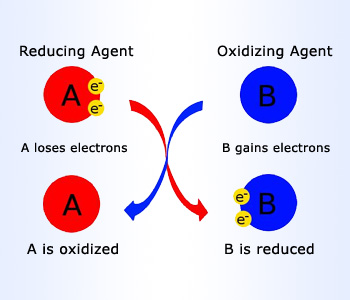
In simple, meaning of oxidation reaction would be an addition of oxygen to a substance or removal of hydrogen of a substance. Oxidation in general is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state of a molecule, atom, or ion.
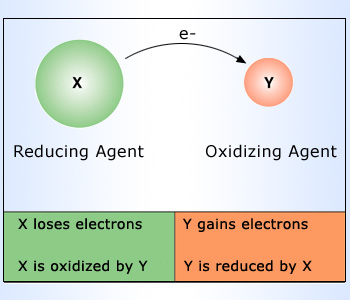
A substance which brings out oxidation of another substance, is called as an oxidizing agent or an oxidant. Oxidizing agent is also defined as a substance, which forces another substance to lose electrons and in turn it gains the electrons. For example, O2, Cl2, F2. Non – metals are borrowers of electrons and can therefore act as oxidants or oxidizing agents.
Cl2 as an oxidizing agent:
Cl2(aq) + 2Br−(aq) → 2Cl−(aq) + Br2(aq)
Oxidation half reaction:
2 Br−(aq) → Br2(aq)
Oxidation States: −1 0
Reduction Half Reaction:
Cl2(aq) → 2Cl−(aq)
Oxidation States: 0 −1
Br− loses an electron; it is being oxidized from Br− to Br2. Thus Br− is the reducing agent.
Cl2 gains one electron; it is being reduced from Cl2 to 2Cl−. Thus Cl2 is the oxidizing agent.

F2 as an oxidizing agent:
In reaction between hydrogen and fluorine, hydrogen is being oxidized by Fluorine.
H2 + F2 → 2HF
oxidation Half reaction:
H2 → 2 H+ + 2e−
reduction Half reaction:
F2 + 2 e− → 2F−
In oxidation half reaction hydrogen is oxidized to an oxidation state of +1 from zero oxidation state and in reduction half reaction fluorine is reduced from an oxidation state of zero to an oxidation state of −1. Thus in the above reaction fluorine acts as an oxidizing agent and H2 acts as an reducing agent.