Worked out example
Ion–electron method for Basic or Neutral solutions:
For Example: The reaction between permanganate ion and iodide ions occurs in neutral solutions. The unbalanced skeleton reaction is
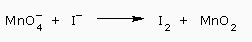
The obvious pairs for the half reactions are:
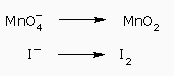
In the second half reaction the iodine atoms needed to be balanced:
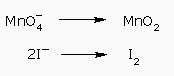
The first half–reaction needs two water molecules to balance the oxygen atoms:
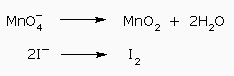
Four hydrogen ions on left side of first–half reaction balances the hydrogen atoms
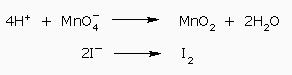
The next step is the balancing of charges. We find that the first half reaction has a total charge of +3 on the left and 0 on the right, while the second half–reaction has a total charge of –2 on the left and 0 on the right. We add three electron to the first half reaction on the left and two electrons to the second half reaction on the right:
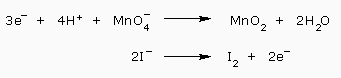
To equalize the electrons, we, multiply the first half reaction by 2 and the second half reaction by 3
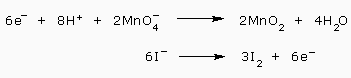
We add the equations
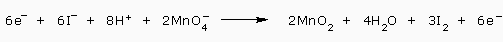
And cancel the 6 electrons
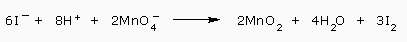
This reaction is balanced in acidic solution. To convert to a basic solution, we use step 7 i.e., add 8OH- ions to each side.
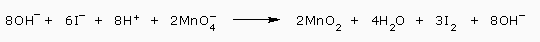
The 8H+ and 8OH- on the left are combined to make 8H2O.

We then cancel 4H2O from each side to simplify the final equation:
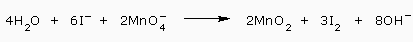
Therefore, the balanced equation for neutral solution of permanganate ion and iodide ions is thus obtained by the Ion–electron method.