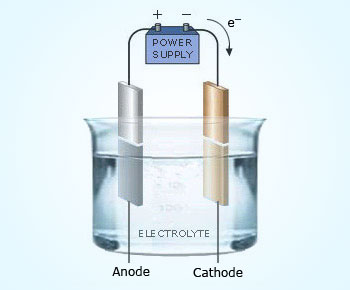
 Typical Electrolytic cell
Components of an electrolytic cell are, a voltaic cell (Battery) which supplies electrical energy, two metallic electrodes (Anode and Cathode) and electrolytic solution.
Typical Electrolytic cell
Components of an electrolytic cell are, a voltaic cell (Battery) which supplies electrical energy, two metallic electrodes (Anode and Cathode) and electrolytic solution.
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell in which the energy from an applied voltage is used to drive a chemical reaction or otherwise a non–spontaneous chemical reaction.
Applying a reverse voltage to a voltaic cell could produce an electrochemical cell which results in electrolysis. It is the process of chemical decomposition of an electrolyte in solution or in the fused state by the passage of electric current. It uses electrical energy to produce chemical change.
The recharging of a car battery is an example of electrolysis.
Another common electrolysis is seen when an electric current is passed through water, a process occurs that breaks the water down into its elemental components. Pure water is a non – conductor of electricity. But if an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is dissolved in it, the solution will start conducting.
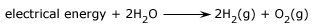
When an electric current is passed through a chemical compound, some compounds are able to conduct electricity. The compound dissociates into ions under the influence of the electric current. The electrical current initiates a chemical reaction or a break up.
 Electrolysis of water
An electrical power is connected to two platinum electrodes which are placed in water. A Hofmann voltameter is often used as demonstration of stoichiometric principles as the two to one ratio of the volumes of hydrogen and oxygen gas produced by the apparatus illustrates the chemical formula of water, H2O.
Electrolysis of water
An electrical power is connected to two platinum electrodes which are placed in water. A Hofmann voltameter is often used as demonstration of stoichiometric principles as the two to one ratio of the volumes of hydrogen and oxygen gas produced by the apparatus illustrates the chemical formula of water, H2O.
Electrolysis of Water
The apparatus or the electrolytic cell, required for performing electrolysis of water is shown in the figure . The cell is called Hoffman's voltameter.
Since water is a covalent compound, pure or distilled water is a non – electrolyte. A few drops of ionic compound like dilute sulfuric acid or few crystals of sodium chloride (NaCl) are enough to make water an electrolyte. The Hoffman voltameter consists of platinum electrodes. The anode and cathode are connected to a battery. The cell produces a small current of the order of a few milliamperes and you will see bubbles appearing in the two arms of the voltameter. The anode collects oxygen and the cathode arm collects hydrogen gas.
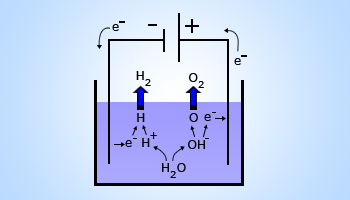 Electrolysis
Splitting water with electricity to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
Electrolysis
Splitting water with electricity to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
The overall reaction that takes place is:
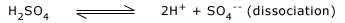
In the presence of these ions, water attains capability of dissociation.

Reaction at the cathode:

Reaction at the anode:
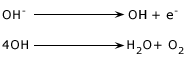
At the anode OH–ions are released in preference to SO4–– ions. This is because it is easier for an OH– ion to give up an electron quickly than the SO4–– ion to do so. Since the sulfuric acid itself does not participate in the chemical reaction that is taking place, it can be called as a catalyst of the reaction.
Any ionic compound will also be able to initiate electrolysis of water, but acidulated water is the best way to achieve electrolysis of water.