 Speed is the distance covered by within the specified time
Speed is the distance covered by within the specified time
Rate is the change in magnitude of a physical quantity with respect to time. For example, 'speed' is the distance covered by a body within the specified time.
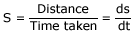 Here distance is a physical quantity (ds) which represents the change in position)
Here distance is a physical quantity (ds) which represents the change in position)
 The wide range of reaction rates. Reactions proceed at a wide range of rates. An explosion (A)
is much faster than the process of ripening (B), which is much faster than the process of rusting (C), which is much faster
than the process of human aging (D).
The wide range of reaction rates. Reactions proceed at a wide range of rates. An explosion (A)
is much faster than the process of ripening (B), which is much faster than the process of rusting (C), which is much faster
than the process of human aging (D).
Like that rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration of reactants or products with respect to time.
We know that any reaction can be represented by the general equation
reactants 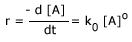 products
products
This equation tells us that during the course of a reaction, reactants are consumed while products are formed. As a result, we can follow the progress of a reaction by monitoring either the decrease in concentration of the reactants or the increase in concentration of the products.
Consider the following reaction (manufacture of ammonia by Haber's process):
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
Rate of disappearance of
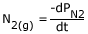
Rate of disappearance of
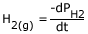
Rate of appearance of
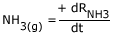
But, the rate of reaction is different from the above equation, as stated above we should consider the stoichiometric representation of reactants and products.
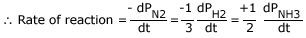
Note: Since this is a gaseous reaction, pressures are taken into consideration instead of concentration in the rate of reaction.
 When you add dilute H2So4 to a sucrose solution nothing will happen. When you
increase the concentration of H2So4 the charring will start. When you add absolute concentration
(98% w/w) to sucrose solute it burns/chars fast, sometimes it catches fire. This experiment shows the effect of concentration
on rate of reaction.
When you add dilute H2So4 to a sucrose solution nothing will happen. When you
increase the concentration of H2So4 the charring will start. When you add absolute concentration
(98% w/w) to sucrose solute it burns/chars fast, sometimes it catches fire. This experiment shows the effect of concentration
on rate of reaction.
Based on the time that we are taking into consideration mathematically rate of reaction is classified into two types.
- Average Rate: Change in concentration with in total time (or a
large time gap) taken for the reaction.
i.e; Δt = tfinal − tinitial - Instantaneous Rate: Rate of reaction at any time during the course
of reaction i.e When Δt → 0, The rate of reaction is called instantaneous
rate. Mathematically it can be obtained from the slope of curve drawn for concentration
v/s time.
Instantaneous Rate =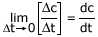
Units of Rate of Reaction:
- Units of rate of reaction are concentration time−1.
- If concentration is in mol L−1 and time is in seconds then the units will be mol L−1s−1.
- When the concentration of gases is expressed in terms of their partial pressures, then the units of the rate of reaction equation will be atm.s−1.
 • Number of collisions / rate of collisions is very high in a gaseous reactions when compare to the reactions occurred
in liquid state.
• Number of collisions / rate of collisions is very high in a gaseous reactions when compare to the reactions occurred
in liquid state.• Formation of NaCl from Na+ and Cl− is simple combination. They are oppositely charged ions, so it is a fast reaction.
Factors effecting rates of reaction:
Nature of Reactants:
- Based on Physical property: Large number of collisions takes place between the reactants when it is a
gaseous reaction. Hence gases are more reactive than solids and liquids.
Order of reactivity: Gases> Liquids > Solids - Based on chemical property: Ionic reactions are faster than covalent reactions. In a covalent reaction for breaking bonds, definite quantity of energy is required [around 40 – 400 KJ]. Hence, the covalent reactions proceed at a lower rate.
Concentration:
Concentration is the major factor influencing the rate of a given reaction. Concentration effect is important because chemical
reactions are usually carried out in solutions.
The rates of both homogenous and heterogeneous reactions are affected by the concentrations of the reactants.
Rate ∝ collision frequency ∝ concentration.
In a simple reaction, reactant molecules collide and form product molecules in one step, but even the rates of complex reactions
depend on reactant concentration.
 A catalytic converter fixed to automobiles which increase the rate of burning of fuels then increase the
efficiency. It also detoxifies the pollutants by converting them into harmless gases
A catalytic converter fixed to automobiles which increase the rate of burning of fuels then increase the
efficiency. It also detoxifies the pollutants by converting them into harmless gases
Temperature:
Temperature often has a major effect on reaction rate. Raise in the temperature increases the reaction rate by increasing the
number of collisions and especially the energy of the collisions. The fact that temperature affects the kinetic energy of the
molecules, and thus the energy of the collisions.
Rate ∝ collision frequency ∝ temperature
Presence Of Catalysts:
Catalysts play a major role on reaction rates. These are the substances, which increases the rates of chemical reactions without
being used up.
 Rate of photosynthesis increases with intensity of light
Rate of photosynthesis increases with intensity of light
Radiation:
Reactions which are taking place in presence of sunlight are known as photochemical reactions.
If the intensity of light radiation is increased the number of photons absorbed by reacting molecules increased. Hence,
rate of product formation also increased.
Rate(r) ∝ Intensity(I)