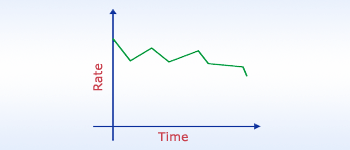
 Rate v/s Time
In reality lot of factors effect the rate of reaction. Some times the rate is fast and sometimes it is slow,
it is always fluctuating.
Rate v/s Time
In reality lot of factors effect the rate of reaction. Some times the rate is fast and sometimes it is slow,
it is always fluctuating.
When studying a chemical reaction, it is important to consider not only the chemical properties of the reactants, but also the conditions under which the reaction occurs, the mechanism by which it takes place, the rate at which it occurs, and the equilibrium toward which it proceeds.
Law Of Mass Action (LOMA) which was proposed by Guldberg and Waage gives the quantitative relationship between rate of reaction and concentration of reactants.
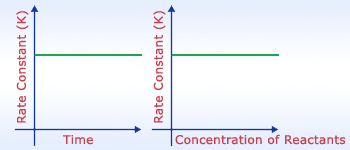 Rate const. v/s Time and Rate const. v/s Concentration
Rate constant is always constant. It is independent of concentration of products or reactants. It is
constant for particular reaction at particular temperature
Rate const. v/s Time and Rate const. v/s Concentration
Rate constant is always constant. It is independent of concentration of products or reactants. It is
constant for particular reaction at particular temperature
LOMA:
Rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of molar concentration (or) active masses of reactants.
According to LOMA, consider the following reaction
A → P
Rate of reactions(r)=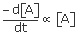
∴ r = K[A]
where K is the rate constant. Suppose, concentration of A is one unit (1 mole/lit)
r = K[1]
⇒ r = K
∴ Rate constant can be defined as rate of a reaction when the concentration of a reactant is one unit.