 Formation of water
Formation of water

In the above reaction Hydrogen (H2) and Oxygen (O2) are reactants and water (H2O) is the product.
Chemicals are everywhere, all the substances in the world are chemicals. The rocks, the plants, the animals, all are made up of chemicals.
Look around yourself. Rusting of iron objects on exposure to damp air, growth of a child, ripening of a fruit, the changing of milk into curd, the digestion of food in our body are some of the examples of chemical reactions.
When wood burns, heat is released. The end product is ash. This happens because the chemicals in the wood change on heating. The chemicals in the wood change into something different (ash) from wood.
Chemical equations:
A simple way to depict a chemical reaction is a chemical equation. Chemical reactions are easily and lucidly represented by
chemical equations. The two sides of the equations use molecular formulae of the participating substances and the new chemicals
formed. Reactants are written on the left–hand side and products are written on the right hand side of the equation. An
arrow indicates the direction in which the reaction is proceeding. The arrow points from the reactants to the product direction.
There are chemical reactions where you won't see a simple arrow but a double arrow (↔) the arrow faces products as well
as reactants. Such a double arrow indicates that the products recombine to give rise to reactants again!!
These chemical reactions are not very common and are called reversible reactions.
Important points to remember while writing chemical reaction are :
- The reactants are written on the left side of the arrow and the products are written on the right side.
- The arrow shows the direction of the reaction.
- The number of atoms of each element involved in the reaction should remain constant.
- The number of molecules of each chemical is represented by a numerical coefficient, which should be a whole number.
- An arrow pointing downward indicates the formation of a product in the form of a precipitate (↓) and an arrow pointing upward shows the release of a gaseous product (↑).
- The physical state of the chemicals may be written near the formula by using standard short forms such as (s) ––– solid ; (l) ––– liquid ; (g)––– gas or vapor and (aq. ) ––– aqueous solution.
While writing down a chemical reaction, the chemical formula written down should indicate stable chemicals.
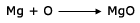
It is incorrect even if the equation is balanced. Oxygen is a stable molecule as O2 and not as O. The correct way to write the above equation is

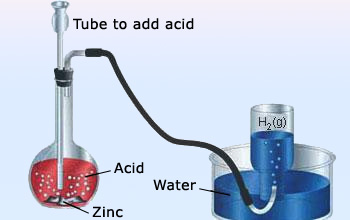 Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc to evolve hydrogen gas
This chemical reaction can be performed in the laboratory as follows:
Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc to evolve hydrogen gas
This chemical reaction can be performed in the laboratory as follows:i) Take some zinc granules in a conical flask(or a test–tube).
ii) Add dilute sulphuric acid over zinc granules.
iii) We can observe bubbles of hydrogen gas being formed around zinc granules.
iv) If we touch the conical flask with our hand, we can feel a sense of hotness as there is a rise in temperature. So, a change in temperature also occurs in this chemical reaction.
 Formation of a Precipitate
Precipitation is the formation of an insoluble product. When colorless solutions of lead nitrate and
potassium iodide are mixed, then a yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed.
Formation of a Precipitate
Precipitation is the formation of an insoluble product. When colorless solutions of lead nitrate and
potassium iodide are mixed, then a yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed.A yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed, when potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate. This chemical reaction can be carried in the laboratory by the following steps:
- Take some lead nitrate solution in a test–tube.
- Add potassium iodide solution to it.
- A yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed at once.
- A change in color also takes place in this chemical reaction.
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions:
The important characteristics of chemical reactions:
- Evolution of a gas
- Formation of a precipitate
- Change in color
- Change in temperature
- Change in state
1. Evolution of a Gas:
There are number of reactions in which gas is evolved. Metals react with acid to liberate gas. For example zinc will react
with dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid to give hydrogen. So, the chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric
acid is characterized by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
2. Formation of a Precipitate:
Precipitate: A precipitate is a solid product which separates out from the solution during a chemical reaction. It can also
be formed by passing a gas into an aqueous solution of a substance (like passing carbon dioxide into lime water).
 Change in color
(a) Potassium dichromate solution is orange in color.
Change in color
(a) Potassium dichromate solution is orange in color.(b) When sulphur dioxide gas is passed through potassium dichromate solution, the orange color of potassium dichromate solution changes to green.
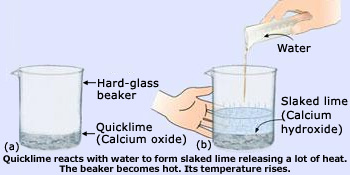 Reaction of quick lime (CaO) with water is an exothermic reaction
The reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature
(which is rise in temperature). The reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is an exothermic reaction
(heat producing reaction). This chemical reaction can be done as follows:
Reaction of quick lime (CaO) with water is an exothermic reaction
The reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature
(which is rise in temperature). The reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is an exothermic reaction
(heat producing reaction). This chemical reaction can be done as follows:
- Take a little of quicklime in a hard–glass beaker
- Add water to it slowly
- Touch the beaker carefully
- The beaker feels to be quite hot(Its temperature is high)
3. Change in color:
Some chemical reactions are characterized by a change in color. For example: When citric acid reacts with potassium
permanganate solution, then the purple color of potassium permanganate solution disappears (it becomes colorless). So,
the chemical reaction between citric acid and purple colored potassium permanganate solution characterized by a change in color
from purple to colorless.
4. Change in temperature:
Some chemical reactions are characterized by a change in temperature.
Why temperature changes takes place in chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions often produce heat energy. When a chemical reaction produce heat energy, then the temperature of reaction
mixture rises and it becomes hot. In few cases, however, chemical reactions absorb heat energy. When a chemical reaction
absorbs heat energy, then the temperature of reaction mixture falls and it becomes cold.
There are two basic types of reactions, when energy changes are considered. They are:
- Exothermic reactions and
- Endothermic reactions
Exothermic reactions release energy as the reaction proceeds. For endothermic reactions, the energy has to be supplied to make the reaction possible.When food is cooked, it is an endothermic reaction and when milk is changing into curd, it is exothermic reaction.