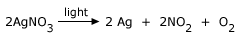
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.
Chemicals are everywhere, all the substances in the world are chemicals. The rocks, the plants, the animals, all are made up of chemicals. Look around yourself. Rusting of iron objects on exposure to damp air, growth of a child, ripening of a fruit, the changing of milk into curd, the digestion of food in our body are some of the examples of chemical reactions.
Types of chemical reactions:
Most of the chemical reactions can be classified into one of the following four types:
- Combination reaction (or synthesis/addition reaction).
- Decomposition reaction.
- Substitution reaction (or displacement reaction).
- Double decomposition reaction.
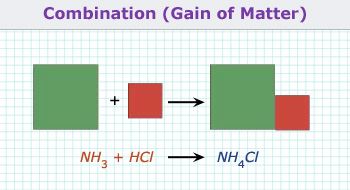
1. Combination reaction:
When two reactants combine to give a new compound, then the reaction is known as combination reaction (or synthesis or
addition reaction).
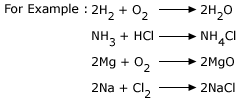
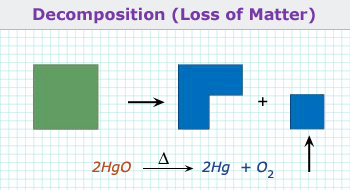
2. Decomposition reaction or Elimination Reaction:
When a single compound breaks up into more than one product, the reaction is known as decomposition reaction. Generally
decomposition occurs when heat is supplied.
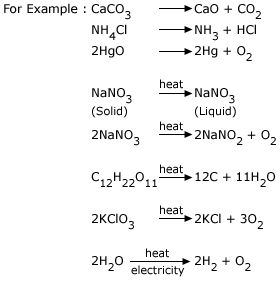
3. Substitution reaction:
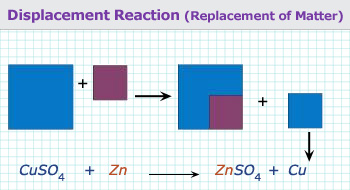
When one element replaces (or displaces) another from a compound, the reaction is known as substitution reaction. In
substitution or displacement reactions one element displaces another by virtue of it being more reactive.
An example below illustrates a typical displacement reaction:
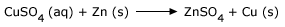
Blue copper sulphate solution reacting with solid zinc will give rise to colorless zinc sulphate solution and solid copper. Thus Zn displaces Cu in the salt form. Zn is more reactive than Cu.
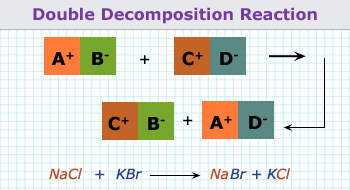
4. Double decomposition reaction:
When the reactants in a chemical reaction, exchange groups while making the products, the reaction is described as double
decomposition reaction.
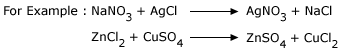
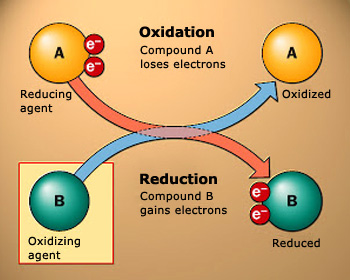 An oxidation reaction is the one where an atom or ion loses electrons. Similarly a reduction reaction is
a reaction where an atom or an ion gains extra electrons. Oxidizing and reducing agents are those substances or compounds
that accept and donate electrons, respectively
An oxidation reaction is the one where an atom or ion loses electrons. Similarly a reduction reaction is
a reaction where an atom or an ion gains extra electrons. Oxidizing and reducing agents are those substances or compounds
that accept and donate electrons, respectively
Other types of reactions :
- Oxidation–reduction reactions
- Neutralization reaction
- Isomerization reactions
Oxidation–reduction reactions:
In oxidation reaction, oxygen is added to, or hydrogen is removed from a compound. In a reduction reaction, oxygen is removed
from, or hydrogen is added to, a compound.
Example below discusses these concepts in detail:

Here Zn atom donates two electrons i.e.,

Zn is donating electrons, hence it is a reducing agent. Zn itself is getting oxidized.
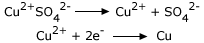
Cu is accepting electrons, hence it is an oxidizing agent. Cu itself is getting reduced.Oxidation– reduction reactions are also known as redox reactions.
 A burning candle is an example of combustion reaction
A burning candle is an example of combustion reaction
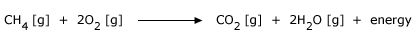
Combustion Reactions:
Combustion or burning is a chemical reaction that occurs between a fuel and an oxidizing agent that produces energy, usually
in the form of heat and light.
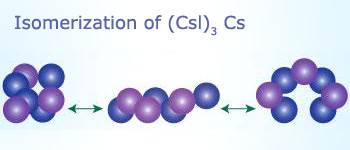 Isomerization
Cesium iodide (CsI) is in cubic cluster form as shown in the above image. At temperatures only slightly
above room temperature, these particles transform rapidly between those three forms.
Isomerization
Cesium iodide (CsI) is in cubic cluster form as shown in the above image. At temperatures only slightly
above room temperature, these particles transform rapidly between those three forms.
Isomerization reactions:
Chemical reactions where rearrangements of atoms occur within a substance without any change in the molecular formula are
called isomerization reactions.
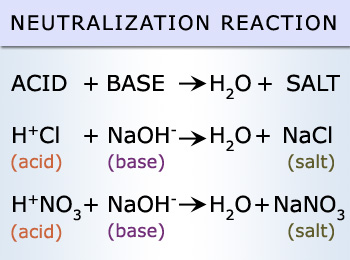
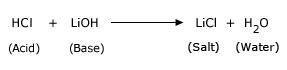
Neutralization Reactions:
These reactions are special type of double–replacement reaction. These reactions are exothermic reactions. Neutralization
reaction is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt. Water is frequently, but not necessarily,
produced as well. A typical neutralization reaction is,
 Silver nitrate is stored in dark colored bottles
Silver nitrate is stored in dark colored bottles
Photochemical reactions:
In some reactions, light energy is used to start the reaction and bring about a chemical change. Such reactions are known
as photochemical reactions. Photosynthesis is a good example of this type of reaction.