 Sodium Hydroxide, Potassium Hydroxide
Sodium Hydroxide, Potassium Hydroxide
Alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Alkalis are best known for being bases that dissolve in water. (Most common form is hydroxide.)
A base is most commonly thought of as an aqueous substance that can accept H+ ions. A soluble base is also often referred to as an alkali if hydroxide ions (OH−) are involved.
Properties of Bases:
- Taste bitter.
- Feel slippery or soapy
- Bases don't change the color of litmus; they can turn red (acidified) litmus back to blue
- Their aqueous (water) solutions conduct and electric current (are electrolytes)
- React with acids to form salts and water
Classification of Bases:
Bases are divided into various types depending upon the acidity or strength of the base:
Classification on the basis of acidity:
Acidity of a base is the number of hydroxyl ions produced by the dissociation of one molecule of the base in aqueous solution.
Depending upon the number of hydroxyl groups or acidity of a base, they are divided into three types.
Mono–acid base: Base which produces only one hydroxyl group per molecule when dissolved
in water is known as mono–acid base.
NaOH  Na+ + OH−
Na+ + OH−
KOH  K+ + OH−
K+ + OH−
 Calcium hydroxide, Magnesium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide, Magnesium hydroxide
Di–acid base: Base which produces two hydroxyl groups per molecule when dissolved
in water is known as di–acid base.
Ca(OH)2  Ca+2 +
2OH−
Ca+2 +
2OH−
Mg(OH)2  Mg+2 +
2OH−
Mg+2 +
2OH−
 Aluminum hydroxide, Chromium hydroxide
Aluminum hydroxide, Chromium hydroxide
 Ammonium hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide
Tri–acid base: Base which produces three hydroxyl groups per molecule when dissolved
in water is known as tri–acid base. Al(OH)3 and Fe(OH)3 are some of the examples in which one mole
requires three mole of a base (NaOH) for complete neutralization.
Al(OH)3  Al3+ +
3OH−
Al3+ +
3OH−
Cr(OH)3  Cr3+ +
3OH−
Cr3+ +
3OH−
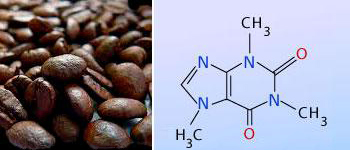 The active ingredient that makes tea and coffee valuable to humans is caffeine. Caffeine is an alkaloid,
a class of naturally occurring compounds containing nitrogen and having the properties of an organic amine base.
The active ingredient that makes tea and coffee valuable to humans is caffeine. Caffeine is an alkaloid,
a class of naturally occurring compounds containing nitrogen and having the properties of an organic amine base.
Classification based on strength: On the basis of strength they are divided into:
- Strong bases: Bases which produce large number of hydroxyl ions in aqueous solution are called strong bases. The hydroxides of the Group I and Group II metals usually are considered to be strong bases.
- Weak bases: Bases which produce only a few hydroxyl ions when dissolved in water are called weak bases. As Bronsted–Lowry bases are proton acceptors, a weak base may also be defined as a chemical base in which protonation is incomplete.