 Nephron is the basic unit of the kidney
Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
Nephron is the basic unit of the kidney
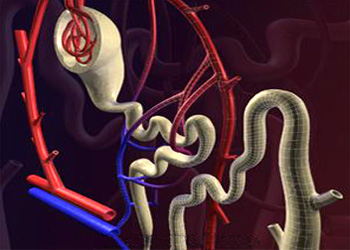
Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. The nephron is the basic unit of the kidney. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. A nephron eliminates wastes from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites and regulates blood pH. Its functions are vital to life and are regulated by the endocrine system by hormones such as anti – diuretic hormone, aldosterone and parathyroid hormone. The Bowman's capsule and the glomerulus together are called Malpighian capsule or just renal capsule. Proximal convoluted tubule is the first twisted region of the tubule after the Bowman's capsule. A long, hairpin loop after the proximal tubule, is called loop of Henle. Second twisted portion of the nephron after the loop of Henle is called distal convoluted tubule. Collecting duct is the long straight portion after the distal tubule that extends from the cortex down through the medulla.
Thus, the nephron is the basic functional and structural unit of the kidney. Its main function is to regulate the amount of water and soluble substances by filtering the blood and reabsorbing what is needed. The kidney's functions are vital to living and are regulated by the endocrine system.