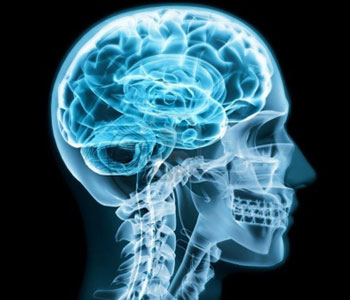
 The skull is the bony structure that encases the brain.
The skull is the bony structure that encases the brain.
The axial skeleton has 80 bones, occupies the longitudinal axis of the body and is made up of the bones of the head(skull), the ribs, the vertebral column and the sternum.
The skull is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial muscles. The two regions of the skull are the cranial and facial region. The cranial portion is the part of the skull that directly houses the brain with the temporal, frontal, parietal and occipital bones and the facial portion includes the rest of the bones of the skull, the maxilla, or upper jaw, and the mandible, or lower jaw, support the facial features of nose, mouth and eyes.
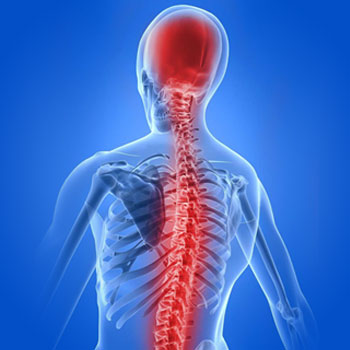 The spinal cord (in red) connects the brain to the nerves throughout the body.
The spinal cord (in red) connects the brain to the nerves throughout the body.
Vertebral column: It is a bony structure found in vertebrates and also known as backbone or spine. It is a flexible column of vertebrae, connecting the trunk of human body to the skull and appendages. It is composed of 33 vertebrae which are divided into 5 regions:
- 7 cervical vertebrae in the neck.
- 12 thoracic vertebrae in the upper back corresponding to each pair of ribs.
- 5 lumbar vertebrae in the lower back.
- 5 sacral vertebrae which are fused together to form 1 bone called the sacrum.
- 4 coccygeal vertebrae that are fused together to form the coccyx or tailbone.
Hence the vertebral formula of man is given as C7T12L5S5CO4.
The rib cage consists of 24 ribs (2 sets of 12), which are attached to a long, flat bone in the middle of the chest called the sternum. The ribs are connected to the sternum with a strong, flexible material called cartilage. It is a bony cage enclosing vital human organs, the heart and lungs.
In vertebrate anatomy, the sternum is a flat bony plate that lies in the middle front part of the rib cage. It is also called breast bone resembling the shape of capital "T" measuring about 15cm long. The sternum in man is present on the ventral part of the chest and acts as a site for attachment of ribs.