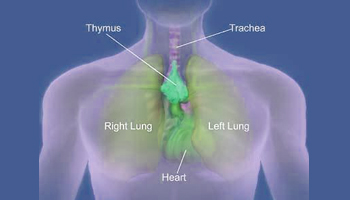
 Thymus is the site of T–cell development and maturation
The function of the thymus is to generate and select a repertoire of T cells that will protect the body from infection. As thymocytes develop an enormous diversity of T–cell receptors.
Thymus is the site of T–cell development and maturation
The function of the thymus is to generate and select a repertoire of T cells that will protect the body from infection. As thymocytes develop an enormous diversity of T–cell receptors.
Primary lymphoid organs: The central or primary lymphoid organs generate lymphocytes from immature progenitor cells.
The thymus and the bone marrow constitute the primary lymphoid tissues involved in the production and early selection of lymphocytes.
The thymus is the site of T–cell development and maturation. It is a flat, bilobed organ situated above the heart. The function of the thymus is to generate and select a repertoire of T cells that will protect the body from infection. As thymocytes develop, an enormous diversity of T–cell receptors is generated by a random process that produces some T cells with receptors capable of recognizing antigen–MHC complexes. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a cell surface molecule encoded by a large gene family in all vertebrates. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or body cells. However, most of the T–cell receptors produced by this random process are incapable of recognizing antigen–MHC complexes and a small portion react with combinations of self antigen–MHC complexes. The thymus induces the death of those T cells that cannot recognize antigen–MHC complexes and those that react with self–antigen–MHC and pose a danger of causing autoimmune disease. More than 95% of all thymocytes die by apoptosis (programmed cell death) in the thymus without ever reaching maturity.
 Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones
In humans, red blood cells are produced in the heads of long bones, in a process known as Hematopoiesis (production of red blood cells). The hematopoietic compartment of bone marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which use the bone marrow vasculature as a conduit to the body's systemic circulation.
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones
In humans, red blood cells are produced in the heads of long bones, in a process known as Hematopoiesis (production of red blood cells). The hematopoietic compartment of bone marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which use the bone marrow vasculature as a conduit to the body's systemic circulation.
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, red blood cells are produced in the heads of long bones, in a process known as Hematopoiesis (production of red blood cells). The hematopoietic compartment of bone marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which use the bone marrow vasculature as a conduit to the body's systemic circulation. Bone marrow is also a key component of the lymphatic system, producing the lymphocytes that support the body's immune system. The red bone marrow is a key element of the lymphatic system, being one of the primary lymphoid organs that generate lymphocytes from immature hematopoietic progenitor cells. The bone marrow and thymus constitute the primary lymphoid tissues involved in the production and early selection of lymphocytes. Furthermore, bone marrow performs a valve–like function to prevent the back flow of lymphatic fluid in the lymphatic system.