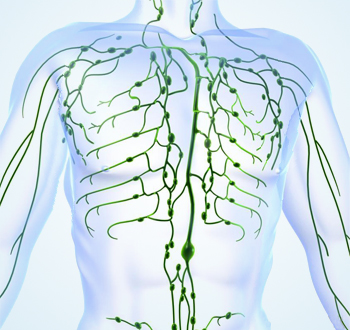
 Lymphatic system is an extensive drainage system that returns water and proteins from various tissues back to the bloodstream.
Lymphatic system is an extensive drainage system that returns water and proteins from various tissues back to the bloodstream.
The lymphatic system is a part of the circulatory system, comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph, unidirectionally towards the heart.
The lymphatic system consists of organs, ducts, and nodes. It transports a watery clear fluid called lymph. This fluid distributes immune cells and other factors throughout the body. It also interacts with the blood circulatory system to drain fluid from cells and tissues. The lymphatic system contains immune cells called lymphocytes, which protect the body against antigens (viruses, bacteria, etc.) that invade the body.
Main functions of lymphatic system
- To collect and return interstitial fluid, including plasma protein to the blood and thus help maintain fluid balance.
- To defend the body against disease by producing lymphocytes.
- To absorb lipids from the intestine and transport them to the blood.
Closely connected with the blood and circulatory system, the lymphatic system is an extensive drainage system that returns water and proteins from various tissues back to the bloodstream.