 Infectious diseases are caused due to infection from germs, most of which are microbes or microorganisms.
Infectious diseases are caused due to infection from germs, most of which are microbes or microorganisms.
Disease is a departure from normal health through structural or functional disorder of the body. Science looks at every disease to be a condition, which has a definite cause and thereby making it possible to prevent it or cure it. Diseases can be broadly classified into two types – infectious diseases and non–infectious diseases.
Infectious diseases:
Diseases which spread from one person to another are called communicable or infectious diseases. Infectious diseases are caused due to infection from germs, most of which are microbes or microorganisms. Louis Pasteur who first stated the 'germ theory of disease', proved that the microbes were present in the air and came from pre–existing microbes. The germs may be virus, bacteria, protozoans, fungus and worms. All these germs are also called "causal organisms" or 'pathogen' and the disease caused by them is infectious disease. Infectious diseases can rapidly spread from one person to another by various means such as by physical contact, water, air, food and insects (vectors). Cholera, diphtheria, typhoid, plague, mumps, cold, malaria, tuberculosis, AIDS are some of the examples.
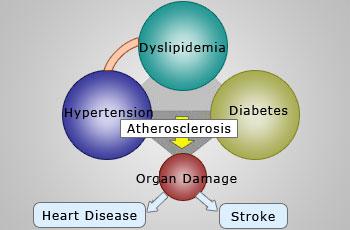 Metabolic Disorders are diseases that disrupt normal metabolism, the process of converting food to energy on a cellular level.
Metabolic Disorders are diseases that disrupt normal metabolism, the process of converting food to energy on a cellular level.
Non–infectious diseases:
Diseases which cannot be spread from person to person and remain confined to the diseased person are called non–communicable or non–infectious diseases. The non–infectious diseases are restricted only to those persons who are suffering from them. These are not spread from infected person to healthy person. Non–infectious diseases may be caused from the lack of certain essential substances in our diet, e.g., proteins, vitamins, minerals (deficiency diseases); general wearing out or degeneration of tissues as in old age (degenerative diseases); uncontrolled growth of tissues in any part of body (cancer); defects in the metabolic reactions (metabolic disorders – diabetes, goiter); and injury and damage to any part of the body by accidents.