 Gel electrophoresis used to separate the DNA molecules
Gel electrophoresis used to separate the DNA molecules
After the lengthy DNA molecule is fragmented, the next step is to separate the DNA fragments. Here is the technique named gel electrophoresis used to separate the DNA molecules.
This technique uses a gel as a molecular sieve to separate nucleic acids or proteins on the basis of size, electrical charge, and other physical properties. Because nucleic acid molecules carry negative charges on their phosphate groups, they all travel toward the positive electrode in an electric field. Thus, gel electrophoresis separates a mixture of linear DNA molecules into bands, each consisting of DNA molecules of the same length. This process of separating DNA molecules is also referred as restriction fragment analysis.
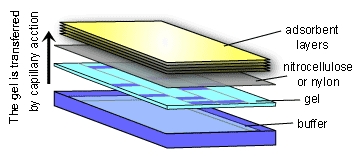 Blotting is the technique in which nucleic acids or proteins are immobilized onto a solid support generally nylon or nitrocellulose membranes.
Blotting is the technique in which nucleic acids or proteins are immobilized onto a solid support generally nylon or nitrocellulose membranes. Blotting Techniques: Blotting is the technique in which nucleic acids or proteins are immobilized onto a solid support generally nylon or nitrocellulose membranes. Blotting of nucleic acid is the central technique for hybridization studies. Nucleic acid labeling and hybridization on membranes have formed the basis for a range of experimental techniques involving understanding of gene expression, organization, etc.
Southern blotting technique is widely used to find specific nucleic acid sequence present in different animals including man. For example if we want to know whether there is a gene like insulin in sea anemone, then DNA of sea anemone is mobilized on membrane and blotted by using insulin probes against it. Southern blotting and hybridization techniques have been employed to detect and screen for genetic diseases and disorders.
Northern blotting technique is widely used to find gene expression and regulation of specific genes. For example if we find human insulin like gene in oyster, then by isolating and immobilizing RNA and blotting it with insulin probe we can tell whether the gene is expressing or not.
Western blotting is another technique where proteins are electrophoresed (separated) in polyacrylamide gel, transferred onto a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane (to which they bind strongly), and the protein bands are detected by their specific interaction with antibodies, lectins or some other compounds.