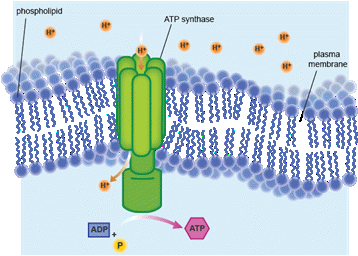
 Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane. Chemiosmosis is accomplished in the presence of the protein complex ATP synthase, which is also located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane. Chemiosmosis is accomplished in the presence of the protein complex ATP synthase, which is also located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient.
More specifically, it relates to the generation of ATP by the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane during cellular respiration.
During the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain, protons accumulate on the inside of the inner mitochondrial membrane. As electrons move from one member of the electron transport chain to the next, protons are transported from one side of the membrane to the other, resulting in a buildup of protons in the intermembrane space.
This creates a charge differential (voltage) across the inner membrane; it is this stored energy that is actually used to synthesize ATP. As these excess protons from the intermembrane space flow back into the mitochondrial matrix(the part of the mitochondrion enclosed within the inner membrane, which houses the enzymes and substrates for the Krebs cycle), ADP is phosphorylated to make ATP (chemiosmosis). Chemiosmosis is accomplished in the presence of the protein complex ATP synthase, which is also located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.