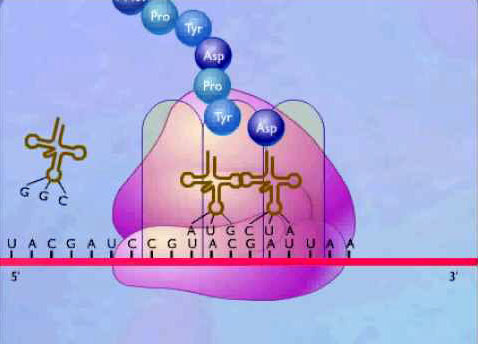
 Protein synthesis – One of the most important biochemical processes of a cell.
Protein synthesis is a series of chemical reactions in which molecules are brought into contact with one another and
chemical bonds are formed and broken.
Protein synthesis – One of the most important biochemical processes of a cell.
Protein synthesis is a series of chemical reactions in which molecules are brought into contact with one another and
chemical bonds are formed and broken. Any chemical reaction involving biomolecules is called a biochemical process.
For example:- all the processes occurring in body of organisms are biochemical processes. It is the study which deals with many complex and interrelated chemical changes. Examples include:
- The chemical reactions by which proteins and all their precursors are synthesized (Protein synthesis).
- Food is converted to energy (metabolism).
- Hereditary characteristics are transmitted (heredity).
- Energy is stored and released.
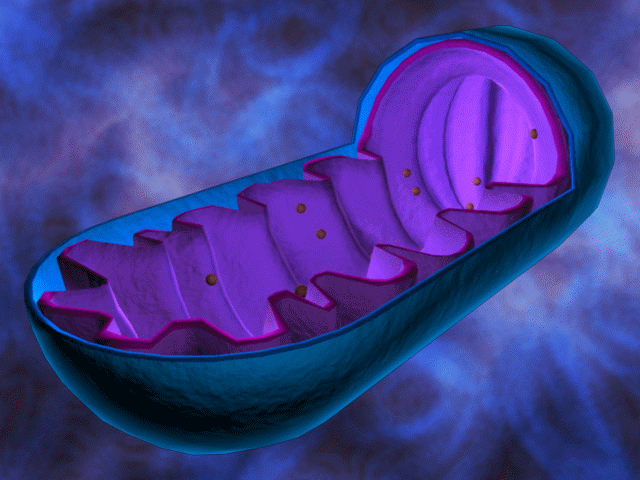 The most prominent role of mitochondria is to produce the energy currency of the cell, ATP –
to regulate cellular metabolism.
The most prominent role of mitochondria is to produce the energy currency of the cell, ATP –
to regulate cellular metabolism.
Protein synthesis: The chemical reactions by which proteins and all their precursors are synthesized is a phenomenon named as Protein synthesis. Protein biosynthesis is the process in which cells build or manufacture proteins.
Lipid biosynthesis: Lipids are small organic molecules made of mostly carbon and hydrogen atoms. They have many forms, and the human body uses them for a variety of essential functions. Testosterone, vitamins A, D, E and K, cholesterol and fat are all considered lipids, and they all serve a specific function in the body. Formation of lipids involves number of biochemical processes.
Metabolism:Metabolism is the set of life–sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme–catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.
Chemical basis of heredity: DNA is the chemical signature of traits that we have inherited from each parent. DNA is the information source for making protein. A section of DNA that provides information for one protein is called gene for that protein. Protein controls the characteristics. Each step involves lot many biochemical processes.